Anti-CD19 CAR-T cells are effective in severe idiopathic Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome
- PMID: 39447569
- PMCID: PMC11604532
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101794
Anti-CD19 CAR-T cells are effective in severe idiopathic Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome
Abstract
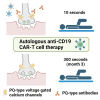
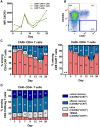
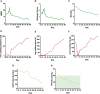
Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is an autoantibody-mediated disease of the neuromuscular junction characterized by muscular weakness. Autoantibodies to presynaptic P/Q-type voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs) induce defective neuromuscular function. In severe cases, current immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory treatment strategies are often insufficient. First reports show beneficial effects of anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy in patients with autoantibody-mediated myasthenia gravis. We report a patient with isolated idiopathic LEMS treated with autologous anti-CD19-CAR-T cells. In this patient, CAR-T infusion leads to expansion of predominantly CD4+ CAR-T cells with a terminally differentiated effector memory cells re-expressing CD45RA (TEMRA)-like phenotype indicating cytotoxic capabilities and subsequent B cell depletion. VGCC antibody titers decrease, resulting in a clinical improvement of LEMS symptoms, e.g., 8-fold increase in walking distance. The patient does not show relevant side effects except for cytokine release syndrome grade 2 and intermittent neutropenia suggesting that anti-CD19 CAR-T cell therapy may be a treatment option in patients with LEMS.
Keywords: B cell autoimmunity; CAR-T cells; CD19; Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome; P/Q-type; VGCC; autoantibody; chimeric antigen receptor; myasthenia gravis; neuroimmunological disorder.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests D.B. is an employee and shareholder of Kyverna Therapeutics with pending patent applications.
Figures


References
-
- Lambert E.H., Eaton L.M., Rooke E.D. Defect of neuromuscular conduction associated with malignant neoplasms. Am. J. Physiol. 1956;187:612–613.
-
- Pinto A., Gillard S., Moss F., Whyte K., Brust P., Williams M., Stauderman K., Harpold M., Lang B., Newsom-Davis J., et al. Human autoantibodies specific for the alpha1A calcium channel subunit reduce both P-type and Q-type calcium currents in cerebellar neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1998;95:8328–8333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.14.8328. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

