Higher risk of recurrence in early-stage breast cancer patients with increased levels of ribosomal protein S6
- PMID: 39448637
- PMCID: PMC11502685
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-75154-1
Higher risk of recurrence in early-stage breast cancer patients with increased levels of ribosomal protein S6
Abstract
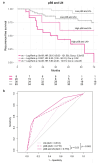
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is implicated in breast cancer progression and recurrence. The identification of PIK3CA and AKT1 mutations and loss of PTEN serve as selection criterion for targeted therapies involving selective inhibitors. However, they do not consistently align with pathway activation, and high-cost determinations limit their routine application. PI3K-downstream epigenetic regulatory mechanisms broaden the alterations that amplify pathway activity and, consequently, sensitivity to selective inhibitors. In this retrospective observational study, conducted within a cohort of early-stage breast cancer patients, we determined phosphorylated ribosomal protein S6 (pS6) at Ser240/244 by immunohistochemistry as an indicator of PI3K pathway activation. Log-Rank test and Cox proportional hazards regression were used to analyze the clinical relevance of pS6, alone and together with clinicopathological variables, regarding recurrence-free survival. ROC curves and the area under the curves were used to evaluate the calibration and discrimination properties of uni- and multivariate models. Our results show that a high percentage of pS6 positive tumor cells was associated with an unfavorable prognosis in a cohort of 129 hormone receptor positive/HER2 negative breast cancer patients (Hazard Ratio = 5.92; Log-Rank p = 9.5e-08; median follow-up = 53 months). When assessed in combination with lymph node status, the predictive capacity was higher compared to both univariate models individually. In conclusion, pS6 could represent a novel independent marker for predicting recurrence risk in luminal breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Immunohistochemistry analysis; PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway; Predictive markers; Prognostic markers; Tumor relapse.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Admoun, C. & Mayrovitz, H. N. in Breast Cancer (ed H. N. Mayrovitz) (2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

