EDNRA affects susceptibility to large artery atherosclerosis stroke through potential inflammatory pathway
- PMID: 39448657
- PMCID: PMC11502785
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-76190-7
EDNRA affects susceptibility to large artery atherosclerosis stroke through potential inflammatory pathway
Abstract
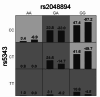
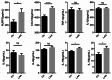
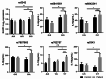
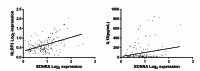
This study aimed to explore the potential association between Endothelin type A receptor (EDNRA) genetic polymorphisms and susceptibility to large artery atherosclerotic stroke (LAA), as well as the involvement of inflammation mechanisms. We recruited Han Chinese patients with LAA and age- and sex-matched controls. The distribution of alleles and genotypes for 16 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in EDNRA was analyzed using dominant, recessive, and co-dominant genetic models between cases and controls. We quantified the mRNA and protein levels of EDNRA and NLRP3 genes, and concentrations of inflammatory factors (TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-18, and CCL18) in peripheral blood samples randomly selected from cases and controls. We also investigated the relationship between these SNPs, gene expression patterns and inflammatory factor levels. A total of 428 LAA cases and 434 controls were enrolled in this study. The results showed that rs5343 TT genotype of EDNRA was significantly associated with an increased risk of LAA (OR = 3.243, 95%CI = 1.608-6.542, P = 0.001). It also demonstrated a significant upregulation level of NLRP3 as well as higher concentrations of IL-10, IL-18, and CCL-18 in cases compared to controls. Besides, we discovered that the EDNRA polymorphisms were linked to NLRP3, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-18 levels in cases. There existed a positive correlation between EDNRA transcription levels and both NLRP3 transcript levels (r = 0.437, p < 0.001) and IL-18 concentrations (r = 0.212, p < 0.001). EDNRA is linked to susceptibility of LAA. This association may be attributed to the NLRP3-mediated inflammatory pathway.
Keywords: EDNRA; Inflammation; Interaction; Large artery atherosclerotic stroke; SNP.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

