The impact of nurse managers' boundary spacing leadership on the relationship between nurses' work embeddedness and innovative work behaviors
- PMID: 39449047
- PMCID: PMC11515436
- DOI: 10.1186/s12912-024-02402-0
The impact of nurse managers' boundary spacing leadership on the relationship between nurses' work embeddedness and innovative work behaviors
Abstract
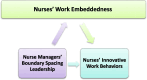
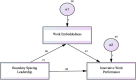
Aim: This study was designed to examine the nurse managers' boundary-spacing leadership's impact on the relationship between nurses' work embeddedness and innovative work behaviors.
Background: In today's evolving healthcare environment, innovation is essential for enhancing patient care, optimizing resources, and supporting healthcare professionals. Nurses are pivotal in driving bedside innovation, but cultivating a culture of innovation within nursing teams involves more than just promoting creative ideas.
Methods: This is a descriptive correlational study that was conducted at one governmental hospital in Tanta, Egypt. Using Nurse Managers Boundary-Spacing Scale for assessing boundary-spacing leadership, The Global Job Embeddedness Scale for measuring work embeddedness, and Innovative Work Behavior Scale for assessing innovative work behavior, 250 nurses were surveyed. Data analysis was run using descriptive and inferential analysis. Correlation and regression analysis were used to examine the study hypotheses.
Results: There is a statistically significant positive relationship between boundary-spacing leadership and work embeddedness (r = 0.615, p < 0.001). Boundary-spacing leadership accounted for 56% of the variance in work embeddedness and 36% of the variance in nurses' innovative work performance. These results highlight the pivotal role of boundary-spacing leadership in both enhancing nurses' work embeddedness and boosting their innovative behaviors. The substantial variance explained by boundary-spacing leadership underscores its critical influence on fostering a supportive and innovative work environment within the nursing field.
Conclusion: Boundary spacing leadership style involves connecting internal and external resources, fostering information exchange, and advocating for the nursing team. While work embeddedness positively correlated with innovative work performance, its impact was less significant than boundary-spacing leadership. This suggests that feeling attached to the organization fosters innovation, but leadership style has a stronger influence. Furthermore, the study found a positive and significant correlation between innovative work performance and both work embeddedness and nurse managers' boundary spacing leadership.
Practical implications: The findings emphasize that boundary-spacing leadership is crucial for enhancing both nurses' work embeddedness and innovative behaviors. Healthcare organizations should focus on developing these leadership skills to create a supportive work environment, foster innovation, and improve staff retention.
Keywords: Boundary Spacing Leadership; Innovative Work Behavior; Nurses; Work Embeddedness.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Marrone J, Quigley N, Prussia G, Dienhart J. Can supportive coaching behaviors facilitate boundary spacing and raise job satisfaction? An indirect-effects model. (2021). J Manag, 01492063211003951.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

