Trabecular Attenuation of L1 in Adult Patients with Multiple Myeloma: An Observational Study on Low-Dose CT Images
- PMID: 39449304
- PMCID: PMC11503432
- DOI: 10.3390/hematolrep16040061
Trabecular Attenuation of L1 in Adult Patients with Multiple Myeloma: An Observational Study on Low-Dose CT Images
Abstract
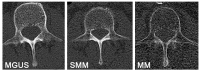
Background: The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of trabecular attenuation of the L1 vertebral body in low-dose CT in adult patients with multiple myeloma (MM), smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM), and monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS).
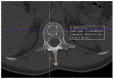
Materials and methods: The study population consisted of 22 patients with MGUS and 51 consecutive patients with newly diagnosed MM (SMM, n = 21; symptomatic MM, n = 36). CT scans were conducted using a 128-slice CT scanner (Somatom go.Top, Siemens, Munich, Germany). Low-dose whole-body CT scans were performed at a single time point for each patient. Trabecular bone density values were obtained by defining regions of interest on non-contrast images at the level of L1 vertebra. A threshold of p = 0.05 was applied to determine statistical significance.
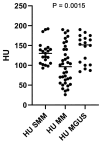
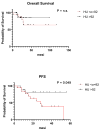
Results: The median Hounsfield unit (HU) value in patients with MGUS, SMM, and MM was 148 HU (range 81-190), 130 HU (range 93-193), and 92 HU (range 26-190), respectively, with a statistically significant difference between the groups (p = 0.0015). Patients with HU values ≤ 92 had lower progression-free survival with statistically significant differences compared to the group with HU values > 92 (p < 0.0499).
Conclusions: This is the earliest evidence of the importance of evaluating L1 attenuation values in low-dose CT images in patients with MGUS, SMM, and MM. Further prospective studies could contribute to reinforcing these results and exploring the clinical applicability and generalization of L1 attenuation values in low-dose whole-body CT scans in routine clinical practice.
Keywords: CT; MGUS; low-dose; multiple myeloma; spine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Can whole-body low-dose multidetector CT exclude the presence of myeloma bone disease in patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS)?Acad Radiol. 2012 Jan;19(1):89-94. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2011.09.016. Acad Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22142681
-
Imaging of Monoclonal Gammapathy of Undetermined Significance and Smoldering Multiple Myeloma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Feb 19;12(2):486. doi: 10.3390/cancers12020486. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32092901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diagnostic value of SE MRI and DWI of the spine in patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, smouldering myeloma and multiple myeloma.Eur Radiol. 2014 Nov;24(11):2754-65. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3324-5. Epub 2014 Aug 9. Eur Radiol. 2014. PMID: 25106487
-
3D osteocyte lacunar morphometry of human bone biopsies with high resolution microCT: From monoclonal gammopathy to newly diagnosed multiple myeloma.Bone. 2024 Dec;189:117236. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2024.117236. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Bone. 2024. PMID: 39151745
-
MGUS and Smoldering Multiple Myeloma: Diagnosis and Epidemiology.Cancer Treat Res. 2016;169:3-12. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-40320-5_1. Cancer Treat Res. 2016. PMID: 27696254 Review.
References
-
- Pierro A., Posa A., Astore C., Sciandra M., Tanzilli A., Petrosino A., del Balso M.S., Fraticelli V., Cilla S., Iezzi R. Whole-Body Low-Dose Multidetector-Row CT in Multiple Myeloma: Guidance in Performing, Observing, and Interpreting the Imaging Findings. Life. 2021;11:1320. doi: 10.3390/life11121320. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gavriatopoulou M., Βoultadaki A., Koutoulidis V., Ntanasis-Stathopoulos I., Bourgioti C., Malandrakis P., Fotiou D., Migkou M., Kanellias N., Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou E., et al. The Role of Low Dose Whole Body CT in the Detection of Progression of Patients with Smoldering Multiple Myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2020;10:93. doi: 10.1038/s41408-020-00360-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

