Polyphenols Regulate the Activity of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals, Having Both Positive and Negative Effects
- PMID: 39449418
- PMCID: PMC11503411
- DOI: 10.3390/jox14040077
Polyphenols Regulate the Activity of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals, Having Both Positive and Negative Effects
Abstract
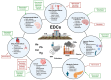
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) are chemical substances that can interfere with any hormone action. They are categorized according to origin and use, such as industrial chemicals like polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs), plastics like bisphenol A (BPA), plasticizers like phthalates, pesticides like dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), fungicides like vinclozolin, and pharmaceuticals like diethylstilbestrol (DES). Natural EDCs, such as phytoestrogens, are present in the diet of both humans and animals. Polyphenols are a large group of natural compounds derived from plants and are found in beverages and food. They are grouped based on their chemical structure into flavonoids and nonflavonoids and are reported to have many beneficial effects on health, including, but not limited to, anticancer, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects. Moreover, polyphenols have both pro- and antioxidant characteristics, and due to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential, they presumably have a protective effect against damage induced by EDCs. However, polyphenols may act as EDCs. In this review, we report that polyphenols regulate the activity of EDCs, having both positive and negative effects. Hence, a better understanding of the associations between EDCs and polyphenols will allow the establishment of improved approaches to protect human health from EDCs.
Keywords: bisphenol-A; cadmium; endocrine disrupting chemicals; phytoestrogens; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

