Circulating Factors as Potential Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Damage Progression Associated with Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 39449501
- PMCID: PMC11503308
- DOI: 10.3390/proteomes12040029
Circulating Factors as Potential Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Damage Progression Associated with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
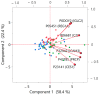
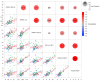
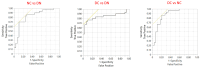
Background: Diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes (T2D), is linked with an increased risk of developing coronary heart disease (CHD). The present study aimed to evaluate potential circulating biomarkers of CHD by adopting a targeted proteomic approach based on proximity extension assays (PEA). Methods: The study was based on 30 patients with both T2D and CHD (group DC), 30 patients with T2D without CHD (group DN) and 29 patients without diabetes but with a diagnosis of CHD (group NC). Plasma samples were analyzed using PEA, with an Olink Target 96 cardiometabolic panel expressed as normalized protein expression (NPX) units. Results: Lysosomal Pro-X carboxypeptidase (PRCP), Liver carboxylesterase 1 (CES1), Complement C2 (C2), and Intercellular adhesion molecule 3 (ICAM3) were lower in the DC and NC groups compared with the DN groups. Lithostathine-1-alpha (REG1A) and Immunoglobulin lambda constant 2 (IGLC2) were found higher in the DC group compared to DN and NC groups. ROC analysis suggested a significant ability of the six proteins to distinguish among the three groups (whole model test p < 0.0001, AUC 0.83-0.88), with a satisfactory discriminating performance in terms of sensitivity (77-90%) and specificity (70-90%). A possible role of IGLC2, PRCP, and REG1A in indicating kidney impairment was found, with a sensitivity of 92% and specificity of 83%. Conclusions: The identified panel of six plasma proteins, using a targeted proteomic approach, provided evidence that these parameters could be considered in the chronic evolution of T2D and its complications.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; targeted proteomics; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zareini B., Blanche P., D’Souza M., Elmegaard Malik M., Nørgaard C.H., Selmer C., Gislason G., Kristensen S.L., Køber L., Torp-Pedersen C., et al. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Impact of Heart Failure on Prognosis Compared to Other Cardiovascular Diseases: A Nationwide Study. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes. 2020;13:e006260. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.119.006260. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shah A.D., Langenberg C., Rapsomaniki E., Denaxas S., Pujades-Rodriguez M., Gale C.P., Deanfield J., Smeeth L., Timmis A., Hemingway H. Type 2 diabetes and incidence of cardiovascular diseases: A cohort study in 1·9 million people. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3:105–113. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70219-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

