UBL3 Interacts with PolyQ-Expanded Huntingtin Fragments and Modifies Their Intracellular Sorting
- PMID: 39449505
- PMCID: PMC11503352
- DOI: 10.3390/neurolint16060089
UBL3 Interacts with PolyQ-Expanded Huntingtin Fragments and Modifies Their Intracellular Sorting
Abstract
Background/objectives: UBL3 (Ubiquitin-like 3) is a protein that plays a crucial role in post-translational modifications, particularly in regulating protein transport within small extracellular vesicles. While previous research has predominantly focused on its interactions with α-synuclein, this study investigates UBL3's role in Huntington's disease (HD). HD is characterized by movement disorders and cognitive impairments, with its pathogenesis linked to toxic, polyglutamine (polyQ)-expanded mutant huntingtin fragments (mHTT). However, the mechanisms underlying the interaction between UBL3 and mHTT remain poorly understood.
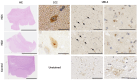
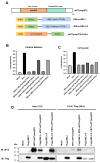
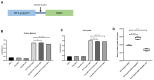
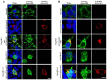
Methods: To elucidate this relationship, we performed hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining and immunohistochemistry (IHC) on postmortem brain tissue from HD patients. Gaussia princeps-based split-luciferase complementation assay and co-immunoprecipitation were employed to confirm the interaction between UBL3 and mHTT. Additionally, we conducted a HiBiT lytic detection assay to assess the influence of UBL3 on the intracellular sorting of mHTT. Finally, immunocytochemical staining was utilized to validate the colocalization and distribution of these proteins.
Results: Our findings revealed UBL3-positive inclusions in the cytoplasm and nuclei of neurons throughout the striatum of HD patients. We discovered that UBL3 colocalizes and interacts with mHTT and modulates its intracellular sorting.
Conclusions: These results suggest that UBL3 may play a significant role in the interaction and sorting of mHTT, contributing to the understanding of its potential implications in the pathophysiology of Huntington's disease.
Keywords: huntingtin protein; huntington’s disease; interaction; polyglutamine; sorting; ubiquitin-like 3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chen B., Hasan M., Zhang H., Zhai Q., Waliullah A.S.M., Ping Y., Zhang C., Oyama S., Mimi M.A., Tomochika Y., et al. UBL3 Interacts with Alpha-Synuclein in Cells and the Interaction Is Downregulated by the EGFR Pathway Inhibitor Osimertinib. Biomedicines. 2023;11:1685. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061685. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

