Effects of polystyrene nano- and microplastics on human breast epithelial cells and human breast cancer cells
- PMID: 39449700
- PMCID: PMC11497447
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38686
Effects of polystyrene nano- and microplastics on human breast epithelial cells and human breast cancer cells
Abstract
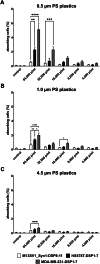
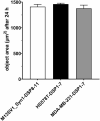
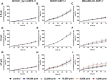
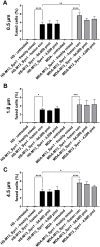
The continuous littering of the environment with plastic and the resulting nano- and microplastics produced from various processes are ever-increasing problems. These materials also affect humans, as the absorption and accumulation of nano- and microplastics and their effects on health have thus far been rarely researched, which also applies to cancer. In the present study, the absorption of different sizes of polystyrene (PS) nano- and microplastics (PS particles) into human breast epithelial cells and human breast cancer cells was investigated. Subsequently, how the proliferation, colony and mammosphere formation abilities, cell fusion and migration of the cells were influenced by the PS particles were investigated. Our data revealed granularity-, dose- and cell line-dependent absorption of the PS particles, with the highest absorption observed in the MDA-MB-231-DSP1-7 cells and the lowest in the M13SV1_Syn1-DSP8-11 cells. Neither the colony-forming ability nor the cell fusion activity increased with the addition of PS particles. In contrast, slight, partially significant stimulatory effects on both proliferation and cell migration were observed, although these effects depended on the particle quantity and size and the cell line used. In summary, PS particles are absorbed by human breast epithelial and human breast cancer cells and influence cells that may be associated with cancer progression.
Keywords: Cancer stem cell properties; Cell fusion; Cell migration; Human breast cancer cells; Human breast epithelial cells; Polystyrene nano- and microplastics.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Masud R.I., Suman K.H., Tasnim S., Begum M.S., Sikder M.H., Uddin M.J., Haque M.N. A review on enhanced microplastics derived from biomedical waste during the COVID-19 pandemic with its toxicity, health risks, and biomarkers. Environ. Res. 2023;216 doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.114434. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stock V., Bohmert L., Lisicki E., Block R., Cara-Carmona J., Pack L.K., Selb R., Lichtenstein D., Voss L., Henderson C.J., Zabinsky E., Sieg H., Braeuning A., Lampen A. Uptake and effects of orally ingested polystyrene microplastic particles in vitro and in vivo. Arch. Toxicol. 2019;93:1817–1833. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02478-7. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

