Protective effects of arecanut seed phenols in retinoic acid induced osteoporosis and the potential mechanisms explored by network pharmacology
- PMID: 39449745
- PMCID: PMC11499182
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1472146
Protective effects of arecanut seed phenols in retinoic acid induced osteoporosis and the potential mechanisms explored by network pharmacology
Abstract
Background: Arecanut seed is an important traditional medicine in Southeast Asia. It has been presented in a clinical formula to treat osteoporosis (OP) in China. Arecanut seed is abundant in phenols. However, most of current studies mainly focused on estrogen-deficient osteoporosis (OP) model of arecanut seed phenols (ASP), there is still a lack of roundly research about molecular mechanism of ASP therapy on OP and its influence on in drug-induced bone loss.
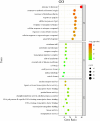
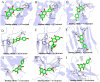
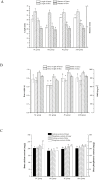
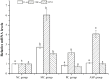
Materials and methods: To explore potential molecular mechanisms and the effects of ASP on OP, network pharmacology, molecular docking methods and a retinoic acid-induced OP rat model were employed in this study. According to the network pharmacology method, OP related targets and ASP compound related targets were collected from databases to obtain hub targets and top active chemicals in ASP treating OP. The potential therapic pathways were also calculated. Binding capacities of top active chemicals to hub targets were analyzed by molecular dock assay. In the animal experiment, osteocalcin (OCN) levels and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity in serum of all the rats were determined. The views of bone section were stained to observe the bone micro-structure of ASP affects. Bone mineral density (BMD), cortical bone thickness (CBT), area ratio of bone cortex (CAR) and area ratio of bone trabecula (TAR) were obtained from micro computed tomography to evaluate the effectiveness of ASP on bone loss.
Conclusion: Three hub genes and three top active compounds were screened by network pharmacology analysis and they combined well with each other. ASP had positive effects on alleviating RA-induced bone loss by regulating the expression of the hub genes. Signals in IL-17 pathway were predicted and primarily verified being potential targets in ASP treating OP.
Keywords: arecanut seed; molecular docking; network pharmacology; osteoporosis; phenols.
Copyright © 2024 Tang, Sun, Song and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Song F, Tang MM, Wang H, Zhang Y, Zhu KX, Chen X, et al. UHPLC-MS/MS identification, quantification of flavonoid compounds from Areca catechu L. extracts and in vitro evaluation of antioxidant and key enzyme inhibition properties involved in hyperglycemia and hypertension. Ind Crops Prod. (2022) 189:115787. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115787 - DOI
-
- Sandhiutami NMD, Fahleni F, Miftahurrohmah N, Widhiyasari NKA, Azalia A, Amalia I. Enhanced wound healing effect of Areca catechu L. ointment via antibacterial activity and anti-inflammatory process at grade IIA burns in rats. J Herbmed Pharmacol. (2023) 12:388–98. doi: 10.34172/jhp.2023.42 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

