Piperlongumine in combination with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of lung cancer cells
- PMID: 39449797
- PMCID: PMC11497197
- DOI: 10.32604/or.2024.053972
Piperlongumine in combination with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of lung cancer cells
Abstract
Objectives: EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) therapies such as erlotinib and gefitinib are approved for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the high incidence of acquired resistance to these EGFR-TKIs may preclude their effectiveness. Piperlongumine (PPL), an extract from the long pepper fruit (Piper longum), has been shown to possess anticancer properties. The purpose of the study was to investigate piperlongumine as an anticancer agent and to study a combination treatment approach with EGFR-TKIs against lung cancer cells.
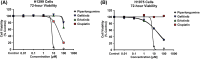
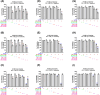
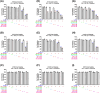
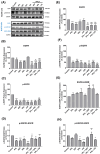
Methods: Anticancer efficacy of PPL, erlotinib (ERL), gefitinib (GEF), and cisplatin (CIS) were investigated in H1299 and H1975 cell lines. Cells were treated with PPL, ERL, GEF, and CIS alone, and in combination, cell viability was determined after 72 h. The mechanism of PPL-induced cytotoxicity was investigated via reactive oxygen species (ROS) induction, and apoptosis induction using acridine orange/ethidium bromide staining and flow cytometry. The effect of treatment on EGFR-mediated oncogenic signaling was investigated by immunoblotting for mitogenic and apoptotic markers.
Results: PPL exhibited a potent cytotoxic effect in H1299 and H1975 cells compared to ERL, GEF, and CIS. Combination treatments of PPL with GEF and ERL showed significant reductions in cancer cells compared to control in both cell lines, which were associated with apoptotic induction, but without significant ROS induction. Compared to control, PPL with GEF significantly increased apoptotic cell death in H1975as confirmed with flow cytometry. Treatment with PPL alone and in combination induced anti-mitogenic and apoptotic responses at the molecular level.
Conclusion: PPL sensitized lung cancer cells to EGFR-TKI and induced potent cytotoxic effects at low concentrations.
Keywords: Mutation; Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); Piperlongumine (PPL); Resistance; Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI).
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study. The authors also declare that the article is an original research work that has not been submitted anywhere else.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer cells: the effect of combining RNA interference with tyrosine kinase inhibitors or cetuximab.BMC Med. 2012 Mar 21;10:28. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-10-28. BMC Med. 2012. PMID: 22436374 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological synergism of 2,2-dichloroacetophenone and EGFR-TKi to overcome TKi-induced resistance in NSCLC cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Nov 15;815:80-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.08.037. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28870456
-
The HSP90 inhibitor ganetespib potentiates the antitumor activity of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition in mutant and wild-type non-small cell lung cancer.Target Oncol. 2015 Jun;10(2):235-45. doi: 10.1007/s11523-014-0329-6. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Target Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25077897 Free PMC article.
-
First-line treatment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 18;3(3):CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33734432 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical utility of erlotinib for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer in Japanese patients: current evidence.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Jul 31;8:1037-46. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S50358. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25114510 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Piperlongumine inhibits renal cell carcinoma progression by modulating the DDX11-miR-15b-3p-DLD axis.Transl Androl Urol. 2025 Apr 30;14(4):897-912. doi: 10.21037/tau-2025-11. Epub 2025 Apr 27. Transl Androl Urol. 2025. PMID: 40376520 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
