Thoracic Radiofrequency Ablation in a Patient With Von Willebrand's Disease: A Case Report
- PMID: 39449872
- PMCID: PMC11500763
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.70102
Thoracic Radiofrequency Ablation in a Patient With Von Willebrand's Disease: A Case Report
Abstract
Congenital bleeding disorders involve specific deficiencies in factors that can alter hemostasis, increasing the risk of bleeding. This case report describes a patient with Von Willebrand's disease who was diagnosed with severe thoracic facet arthritis with pain scores of 9/10. An antihemophilic factor (vWF, Humate-P) injection was administered by a hematologist just before thoracic medial branch blocks. Rather than receiving traditional second thoracic medial branch blocks on another day, the patient, after documenting complete relief of his symptoms with 1% lidocaine, received bilateral T6-8 thoracic radiofrequency ablations, which resulted in complete resolution of his symptoms. A second dose of Humate-P was delivered 24 hours post-procedure. Careful planning with hematologists can enable safe and effective interventional pain procedures in patients with congenital hematologic disorders. This appears to be the first case report in world literature of a patient with Von Willebrand's disease successfully receiving thoracic radiofrequency ablations.
Keywords: ablation; interventional pain; radiofrequency; thoracic medial branch blocks; von willebrand’s disease.
Copyright © 2024, Brandt et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
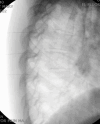
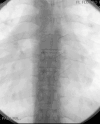
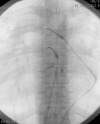
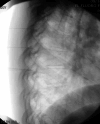
Figures
References
-
- Sabih A, Babiker HM. StatPearls [Internet] Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Von Willebrand disease. - PubMed
-
- Von Willebrand factor (vWF) [ Aug; 2024 ]. 2024. https://diapharma.com/von-willebrand-factor-vwf/ https://diapharma.com/von-willebrand-factor-vwf/
-
- Pitfalls in interventional pain medicine: hyponatremia after DDAVP for a patient with von Willebrand disease undergoing an epidural steroid injection. Khan TW, Yacoub A. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6467090. Case Rep Anesthesiol. 2017;2017:6467090. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health. Pharmacoeconomic Review Report: Von Willebrand Factor (Recombinant) (Vonvendi): (Shire Pharma Canada Ulc, Now Part of Takeda Canada Inc.): Indication: For the Treatment and Control of Bleeding Episodes in Adults Diagnosed With Von Willebrand Disease. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2021. Pharmacoeconomic review report: von Willebrand factor (recombinant) (vonvendi): (shire pharma Canada ULC, now part of Takeda Canada Inc.): Indication: For the treatment and control of bleeding episodes in adults diagnosed with von Willebrand disease (aged ≥ 18), and perioperative management of bleeding in adults diagnosed with von Willebrand disease (aged ≥ 18) . - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous