Addressing the Digital Divide in Health Education: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39449933
- PMCID: PMC11499311
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.70048
Addressing the Digital Divide in Health Education: A Systematic Review
Abstract
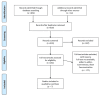
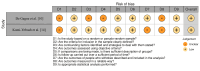
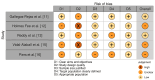
The disparity in access to essential healthcare resources and services is exacerbated by the digital divide, which presents a significant obstacle to health education. Effective tactics to advance digital equity and provide equitable access to resources for telehealth and digital health are needed to close this gap. Digital databases such as PubMed, MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar were used to conduct a systematic review. Keywords and Boolean operators including "digital divide," "health education," "digital equity," "telehealth," "digital health literacy," and "strategies" were used in the literature search process. Only peer-reviewed English-language papers that addressed methods for bridging the digital divide in health education were accepted after being screened in accordance with the preset inclusion and exclusion criteria. The results were compiled using a narrative synthesis method after data were retrieved and synthesized with the aid of suitable quality assessment tools. After satisfying the inclusion criteria, seven papers were added to the systematic review. The results emphasized the complexity of the digital divide in health education and provided a range of approaches to mitigate disparities in access to digital health technologies and resources. The importance of digital equality and universal design, continuous intervention evaluation and monitoring, and enduring obstacles to Internet access and healthcare technology availability were among the major themes. This systematic study emphasizes how critical it is to put evidence-based tactics into practice in order to close the digital divide in health education. Through the promotion of universal design principles, ongoing evaluation of treatments, and digital equity, stakeholders can mitigate health disparities, improve population health, and guarantee equitable access to telehealth and digital health services.
Keywords: digital divide; digital equity; digital health literacy; health education; intervention strategies; telehealth.
Copyright © 2024, Bhoyar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Valdez VB, Javier SP. Reduced Inequalities. Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Cham: Springer; 2021. Digital divide: from a peripheral to a core issue for all SDGs; pp. 88–101.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
