CAR-engineered T cell therapy as an emerging strategy for treating autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 39450112
- PMCID: PMC11500465
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1447147
CAR-engineered T cell therapy as an emerging strategy for treating autoimmune diseases
Abstract
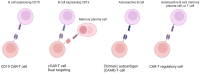
CAR-T therapy has demonstrated great success in treating hematological malignancies, which has led to further research into its potential in treating other diseases. Autoimmune diseases have great potential to be treated with this therapy due to the possibility of specific targeting of pathological immune cells and cells that produce autoantibodies, which could lead to permanent healing and restoration of immunological tolerance. Several approaches are currently under investigation, including targeting and depleting B cells via CD19 in the early stages of the disease, simultaneously targeting B cells and memory plasma cells in later stages and refractory states, as well as targeting specific autoantigens through the chimeric autoantibody receptor (CAAR). Additionally, CAR-engineered T regulatory cells can be modified to specifically target the autoimmune niche and modulate the pathological immune response. The encouraging results from preclinical studies have led to the first successful use of CAR-T therapy in humans to treat autoimmunity. This paved the way for further clinical studies, aiming to evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of these therapies, potentially revolutionizing clinical use.
Keywords: CAAR-T; CAR-T; CAR-Treg; autoimmunity; cell therapy; immunotherapy; regenerative medicine.
Copyright © 2024 Vukovic, Abazovic, Vucetic and Medenica.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

