Case report: A case of sintilimab-induced recurrent diabetic ketoacidosis and thyroid dysfunction in a patient with advanced cervical carcinoma
- PMID: 39450164
- PMCID: PMC11499202
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1405856
Case report: A case of sintilimab-induced recurrent diabetic ketoacidosis and thyroid dysfunction in a patient with advanced cervical carcinoma
Abstract
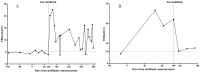
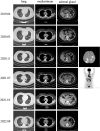
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have radically altered cancer treatment, but immune toxicities called immune-related adverse events (irAEs), particularly endocrine toxicities, such as acute-onset diabetes and thyroid dysfunction, pose challenges. Although most irAEs have mild-to-moderate severity, failure to diagnose and treat them promptly can result in life-threatening complications. This report presents the case of a 50-year-old woman who developed ICI-induced diabetes mellitus (ICI-DM) during sintilimab treatment for advanced cervical carcinoma. The patient experienced repeated episodes of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and subclinical hypothyroidism. Unlike the case of patients with typical type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM), our patient tested negative for β cell autoantibodies and progressed rapidly. Prompt recognition and insulin treatment are crucial for helping patients overcome such crises. Eventually, sintilimab was discontinued, and chemotherapy was initiated. This case report contributes to our understanding of ICI-DM. The significance of monitoring thyroid function and blood glucose levels before initiating ICI treatment to identify irAEs early and effectively manage them are important considerations.
Keywords: DKA; TIDM; immune checkpoint inhibitor; immune-related endocrine event; thyroid dysfunction.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Cai and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures