Tumor-associated macrophages and CD8+ T cells: dual players in the pathogenesis of HBV-related HCC
- PMID: 39450177
- PMCID: PMC11499146
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1472430
Tumor-associated macrophages and CD8+ T cells: dual players in the pathogenesis of HBV-related HCC
Abstract
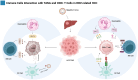
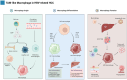
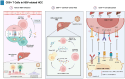
HBV infection is a key risk factor for the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a highly invasive tumor, and is characterized by its persistent immunosuppressive microenvironment. This review provides an in-depth analysis of HBV-related HCC and explores the interactions between neutrophils, natural killer cells, and dendritic cells, examining their roles in regulating tumor-associated macrophages and CD8+ T cells and shaping the tumor microenvironment. Two critical players in the immunosuppressive milieu of HBV-related HCC are CD8+ T cells and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). The study explores how TAMs, initially recruited to combat infection, transform, adopting a tumor-promoting phenotype, turning against the body, promoting tumor cell proliferation, suppressing anti-tumor immunity, and assisting in the spread of cancer. Meanwhile, CD8+ T cells, crucial for controlling HBV infection, become dysfunctional and exhausted in response to persistent chronic viral inflammation. The review then dissects how TAMs manipulate this immune response, further depleting CD8+ T cell functions through mechanisms like arginine deprivation and creating hypoxic environments that lead to exhaustion. Finally, it explores the challenges and promising therapeutic avenues that target TAMs and CD8+ T cells, either separately or in combination with antiviral therapy and personalized medicine approaches, offering hope for improved outcomes in HBV-related HCC.
Keywords: CD8+ T cell; HBV-related HCC; TAMs-like macrophage; hepatitis B virus; immunology; pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2024 Khan, Mao, Hu, Shi, Wang, Rehman and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO . Hepatitis B (2023). World Health organization. Available online at: https://wwwwhoint/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (Accessed Dec 28 2023).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

