Quality-controlled characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific to an EC5-domain of human desmoglein 3 for pemphigus research
- PMID: 39450179
- PMCID: PMC11499099
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1464881
Quality-controlled characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific to an EC5-domain of human desmoglein 3 for pemphigus research
Abstract
Background: Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) is a life-threatening autoimmune blistering disease caused mainly by IgG autoantibodies (auto-abs) against the cadherin-type adhesion molecules desmoglein (Dsg) 1 and 3. Pathogenic anti-Dsg3 auto-abs bind to different Dsg3 epitopes, leading, among others, to signalling that is involved in pathogenic events, such as Dsg3 depletion. As central tools in research on PV, a limited number of antibodies such as AK23 are frequently used by the autoimmune bullous disease community.
Methods: Previously, we have introduced a novel Dsg3 EC5-binding antibody termed 2G4 that may potentially serve as a superior tool for numerous PV related analysis. The purpose of this study was to develop a quality-controlled production and verification process that allows I) a continuous quality improvement, and II) a verified and comprehensible overall quality with regard to pathogenic antigen-specific binding in a variety of pemphigus assays for each batch production.
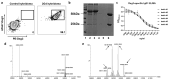
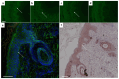
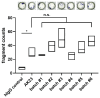
Results: Thus, a workflow based on a standardized operating procedure was established. This includes the verification of purity and in-vitro binding capacity (SDS-page, direct and indirect immunofluorescence) as primary parameters, and size analysis by mass-spectrometry and ex-vivo pathogenicity by monolayer dissociation assay.
Conclusion: We here present an extensive point-by-point quality controlled IgG production protocol, which will serve as a basis for a standardized antibody assessment in PV research.
Keywords: 2G4; PV; antibody; autoimmunity; desmoglein (Dsg); pemphigus vulgaris; quality control.
Copyright © 2024 Eming, Riaz, Müller, Zakrzewicz, Linne, Tikkanen, Zimmer and Hudemann.
Conflict of interest statement
RE is recipient of an unrestricted grant from Topas Therapeutics, Hamburg, Germany. RT has received funding from argenx. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lo AS, Mao X, Mukherjee EM, Ellebrecht CT, Yu X, Posner MR, et al. Pathogenicity and epitope characteristics do not differ in igG subclass-switched anti-desmoglein 3 IgG1 and IgG4 autoantibodies in pemphigus vulgaris. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0156800. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156800 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

