Discovery and Characterization of BAY-184: A New Potent and Selective Acylsulfonamide-Benzofuran In Vivo-Active KAT6AB Inhibitor
- PMID: 39450890
- PMCID: PMC11571114
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c01709
Discovery and Characterization of BAY-184: A New Potent and Selective Acylsulfonamide-Benzofuran In Vivo-Active KAT6AB Inhibitor
Abstract
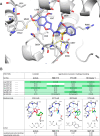
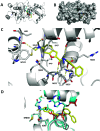
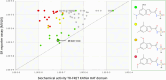
KAT6A and KAT6B genes are two closely related lysine acetyltransferases that transfer an acetyl group from acetyl coenzyme A (AcCoA) to lysine residues of target histone substrates, hence playing a key role in chromatin regulation. KAT6A and KAT6B genes are frequently amplified in various cancer types. In breast cancer, the 8p11-p12 amplicon occurs in 12-15% of cases, resulting in elevated copy numbers and expression levels of chromatin modifiers like KAT6A. Here, we report the discovery of a new acylsulfonamide-benzofuran series as a novel structural class for KAT6A/B inhibition. These compounds were identified through high-throughput screening and subsequently optimized using molecular modeling and cocrystal structure determination. The final tool compound, BAY-184 (29), was successfully validated in an in vivo proof-of-concept study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
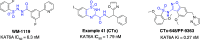

References
-
- Hirsch C. L.; Wrana J. L.; Dent S. Y. R. KATapulting toward Pluripotency and Cancer. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429 (13), 1958–1977. 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.09.023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Voss A. K.; Thomas T. Histone Lysine and Genomic Targets of Histone Acetyltransferases in Mammals. BioEssays 2018, 40 (10), e1800078 10.1002/bies.201800078. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

