Regulation of β-Adrenergic Receptors in the Heart: A Review on Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Heart Failure
- PMID: 39451192
- PMCID: PMC11506672
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13201674
Regulation of β-Adrenergic Receptors in the Heart: A Review on Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Heart Failure
Abstract
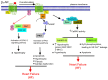
The prolonged overstimulation of β-adrenergic receptors (β-ARs), a member of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family, causes abnormalities in the density and functionality of the receptor and contributes to cardiac dysfunctions, leading to the development and progression of heart diseases, especially heart failure (HF). Despite recent advancements in HF therapy, mortality and morbidity rates continue to be high. Treatment with β-AR antagonists (β-blockers) has improved clinical outcomes and reduced overall hospitalization and mortality rates. However, several barriers in the management of HF remain, providing opportunities to develop new strategies that focus on the functions and signal transduction of β-ARs involved in the pathogenesis of HF. As β-AR can signal through multiple pathways influenced by different receptor subtypes, expression levels, and signaling components such as G proteins, G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs), β-arrestins, and downstream effectors, it presents a complex mechanism that could be targeted in HF management. In this narrative review, we focus on the regulation of β-ARs at the receptor, G protein, and effector loci, as well as their signal transductions in the physiology and pathophysiology of the heart. The discovery of potential ligands for β-AR that activate cardioprotective pathways while limiting off-target signaling is promising for the treatment of HF. However, applying findings from preclinical animal models to human patients faces several challenges, including species differences, the genetic variability of β-ARs, and the complexity and heterogeneity of humans. In this review, we also summarize recent updates and future research on the regulation of β-ARs in the molecular basis of HF and highlight potential therapeutic strategies for HF.
Keywords: CaMKII; G protein; G protein-coupled receptor kinase; adenylyl cyclase (AC); cGMP; heart failure; β-adrenergic receptor (β-AR); β-arrestin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mika D., Bobin P., Lindner M., Boet A., Hodzic A., Lefebvre F., Lechène P., Sadoune M., Samuel J.L., Algalarrondo V., et al. Synergic PDE3 and PDE4 control intracellular cAMP and cardiac excitation-contraction coupling in a porcine model. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2019;133:57–66. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.05.025. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

