Immunomodulatory Functions of TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand in Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 39451194
- PMCID: PMC11506310
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13201676
Immunomodulatory Functions of TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand in Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
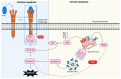
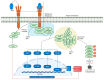
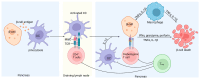
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a member of the TNF protein superfamily and was initially identified as a protein capable of inducing apoptosis in cancer cells. In addition, TRAIL can promote pro-survival and proliferation signaling in various cell types. Subsequent studies have demonstrated that TRAIL plays several important roles in immunoregulation, immunosuppression, and immune effector functions. Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease characterized by hyperglycemia due to the loss of insulin-producing β-cells, primarily driven by T-cell-mediated pancreatic islet inflammation. Various genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors, in conjunction with the immune system, contribute to the initiation, development, and progression of T1D. Recent reports have highlighted TRAIL as an important immunomodulatory molecule with protective effects on pancreatic islets. Experimental data suggest that TRAIL protects against T1D by reducing the proliferation of diabetogenic T cells and pancreatic islet inflammation and restoring normoglycemia in animal models. In this review, we aimed to summarize the consequences of TRAIL action in T1D, focusing on and discussing its signaling mechanisms, role in the immune system, and protective effects in T1D.
Keywords: T cells; TRAIL; apoptosis; autoimmunity; immunoregulation; type 1 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stacey M.A., Marsden M., Pham T.A.N., Clare S., Dolton G., Stack G., Jones E., Klenerman P., Gallimore A.M., Taylor P.R., et al. Neutrophils Recruited by IL-22 in Peripheral Tissues Function as TRAIL-Dependent Antiviral Effectors against MCMV. Cell Host Microbe. 2014;15:471–483. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.03.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grosse-Wilde A., Voloshanenko O., Bailey S.L., Longton G.M., Schaefer U., Csernok A.I., Schütz G., Greiner E.F., Kemp C.J., Walczak H. TRAIL-R Deficiency in Mice Enhances Lymph Node Metastasis without Affecting Primary Tumor Development. J. Clin. Investig. 2008;118:100–110. doi: 10.1172/JCI33061. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

