Preparation of Cassia Bean Gum/Soy Protein Isolate Composite Matrix Emulsion Gel and Its Effect on the Stability of Meat Sausage
- PMID: 39451296
- PMCID: PMC11506983
- DOI: 10.3390/gels10100643
Preparation of Cassia Bean Gum/Soy Protein Isolate Composite Matrix Emulsion Gel and Its Effect on the Stability of Meat Sausage
Abstract
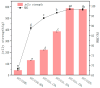
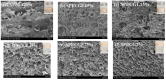
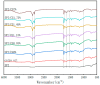
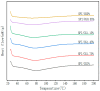
The use of plant-derived emulsified gel systems as fat substitutes for meat products has always been an important direction in the development of healthy foods. In this study, a composite matrix emulsion gel was prepared with soy protein isolate (SPI) and different concentrations of cassia bean gum (CG), and then the selected emulsion gel was applied to meat sausage as a fat substitute to explore its stability. Our results showed that the hardness, chewiness, viscosity, shear stress, and G' and G″ moduli of the emulsion gel increased considerably with the cassia bean gum concentration, the thickness of the emulsion gel increased, and the pore size decreased. The gel strength of the 1.75% CG/SPI emulsion gel was the highest, which was 586.91 g. The elasticity was 0.94 mm, the masticability was 452.94 mJ, and the water-holding capacity (WHC) was 98.45%. Then, the 1.75% CG/SPI emulsion gel obtained via screening was applied as a fat substitute in meat sausage. With an increase in the substitution amount, the cooking loss, emulsification stability, pH, color difference, texture, and antioxidant activity of the meat sausage before and after freezing and thawing increased first and then decreased. The indexes of meat sausage with 50% fat replacement were not considerably different from those of full-fat meat sausage. This study can provide a theoretical basis for the application of plant-derived emulsified gel systems as fat substitutes in meat sausage.
Keywords: cassia bean gum; composite matrix emulsion gel; fat substitute; freeze–thaw stability; meat and sausage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Agar-based composite emulsion gel as a pork fat substitute in sausages: Understanding meat batter stabilization mechanisms based on fat sources.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Jul;318(Pt 1):144851. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.144851. Epub 2025 Jun 1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40460959
-
O/W Pickering emulsions stabilized by Flammulina velutipes polysaccharide nanoparticles as a fat substitute: the effects of phase separation on emulsified sausage's techno-functional and sensory quality.J Sci Food Agric. 2020 Jan 15;100(1):268-276. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10034. Epub 2019 Oct 29. J Sci Food Agric. 2020. PMID: 31512249
-
Flaxseed Gum/Arabic Gum/Tween 80-Based Oleogel as a Fat Substitute Applied in Emulsified Sausage: Physicochemical Properties, Sensory Attributes and Nutritional Quality.Gels. 2023 Sep 18;9(9):759. doi: 10.3390/gels9090759. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37754440 Free PMC article.
-
Freeze-thaw stability of transglutaminase-induced soy protein-maltose emulsion gel: Focusing on morphology, texture properties, and rheological characteristics.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Mar;261(Pt 1):129716. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129716. Epub 2024 Jan 28. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38290624
-
Application of Emulsion Gels as Fat Substitutes in Meat Products.Foods. 2022 Jun 30;11(13):1950. doi: 10.3390/foods11131950. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35804763 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huang X., Liu B., Li Y., Huang D., Zhu S. Influence Mechanism of Components and Characteristics on Structural and Oxidative Stability of Emulsion Gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2024;151:109852. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2024.109852. - DOI
-
- Li M., Feng L., Dai Z., Li D., Zhang Z., Zhou C., Yu D. Improvement of 3D Printing Performance of Whey Protein Isolate Emulsion Gels by Regulating Rheological Properties: Effect of Polysaccharides Incorporation. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024:1–15. doi: 10.1007/s11947-024-03488-9. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

