Shear-Thinning Extrudable Hydrogels Based on Star Polypeptides with Antimicrobial Properties
- PMID: 39451305
- PMCID: PMC11507159
- DOI: 10.3390/gels10100652
Shear-Thinning Extrudable Hydrogels Based on Star Polypeptides with Antimicrobial Properties
Abstract
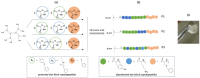
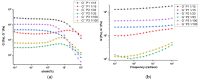
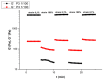
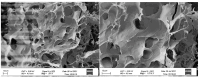
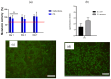
Hydrogels with low toxicity, antimicrobial potency and shear-thinning behavior are promising materials to combat the modern challenges of increased infections. Here, we report on 8-arm star block copolypeptides based on poly(L-lysine), poly(L-tyrosine) and poly(S-benzyl-L-cysteine) blocks. Three star block copolypeptides were synthesized with poly(S-benzyl-L-cysteine) always forming the outer block. The inner block comprised either two individual blocks of poly(L-lysine) and poly(L-tyrosine) or a statistical block copolypeptide from both amino acids. The star block copolypeptides were synthesized by the Ring Opening Polymerization (ROP) of the protected amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides (NCAs), keeping the overall ratio of monomers constant. All star block copolypeptides formed hydrogels and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) confirmed a porous morphology. The investigation of their viscoelastic characteristics, water uptake and syringe extrudability revealed superior properties of the star polypeptide with a statistical inner block of L-lysine and L-tyrosine. Further testing of this sample confirmed no cytotoxicity and demonstrated antimicrobial activity of 1.5-log and 2.6-log reduction in colony-forming units, CFU/mL, against colony-forming reference laboratory strains of Gram-negative Escherichia coli and Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus, respectively. The results underline the importance of controlling structural arrangements in polypeptides to optimize their physical and biological properties.
Keywords: antimicrobial potency; hydrogels; polypeptides; star polymers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Jacquet R., LaBauve A.E., Akoolo L., Patel S., Alqarzaee A.A., Fok Lung T.W., Poorey K., Stinear T.P., Thomas V.C., Meagher R.J., et al. Dual gene expression analysis identifies factors associated with Staphylococcus aureus virulence in diabetic mice. Infect. Immun. 2019;87:e00163-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00163-19. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Macedo G.H.R.V., Costa G.D.E., Oliveira E.R., Damasceno G.V., Mendonça J.S.P., Silva L.S., Chagas V.L., Bazán J.M.N., Aliança A.S.S., de Miranda R.C.M., et al. Interplay between eskape pathogens and immunity in skin infections: An overview of the major determinants of virulence and antibiotic resistance. Pathogens. 2021;10:148. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10020148. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

