Tuning Antioxidant Function through Dynamic Design of Chitosan-Based Hydrogels
- PMID: 39451308
- PMCID: PMC11507920
- DOI: 10.3390/gels10100655
Tuning Antioxidant Function through Dynamic Design of Chitosan-Based Hydrogels
Abstract
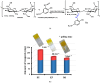
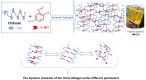
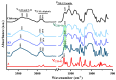
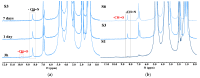
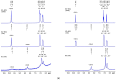
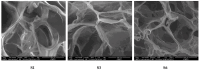
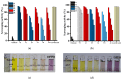
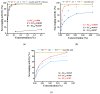
Dynamic chitosan-based hydrogels with enhanced antioxidant activity were synthesized through the formation of reversible imine linkages with 5-methoxy-salicylaldehyde. These hydrogels exhibited a porous structure and swelling capacity, influenced by the crosslinking degree, as confirmed by SEM and POM analysis. The dynamic nature of the imine bonds was characterized through NMR, swelling studies in various media, and aldehyde release measurements. The hydrogels demonstrated significantly improved antioxidant activity compared to unmodified chitosan, as evaluated by the DPPH method. This research highlights the potential of developing pH-responsive chitosan-based hydrogels for a wide range of biomedical applications.
Keywords: antioxidant properties; chitosan; dynamic behavior; hydrogels; imine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Abd El-Ghany N.A., Abdel Aziz M.S., Abdel-Aziz M.M., Mahmoud Z.M. Reinforcement of antimicrobial activity and swelling ability of starch-g-poly 4-acrylamidobenzoic acid using chitosan nanoparticles. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2023;57:803–813. doi: 10.35812/CelluloseChemTechnol.2023.57.71. - DOI
-
- Li M., Mu Y., Xu Q., Jin L., Fu Y. Injectable, Rapid Self-Healing, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Nanocellulose-Tannin Hydrogels Formed via Metal-Ligand Coordination for Drug Delivery and Wound Dressing. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2024;208:117876. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.117876. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

