Development and Evaluation of the Acaricidal Activity of Xantan Gum-Based Hydrogel and Polymeric Nanoparticles Containing Achyrocline satureioides Extract
- PMID: 39451311
- PMCID: PMC11508096
- DOI: 10.3390/gels10100658
Development and Evaluation of the Acaricidal Activity of Xantan Gum-Based Hydrogel and Polymeric Nanoparticles Containing Achyrocline satureioides Extract
Abstract
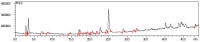
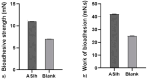
The Rhipicephalus microplus tick causes enormous economic losses in livestock farming around the world. Despite several promising studies carried out with plant extracts such as Achyrocline satureioides against this ectoparasite, a major obstacle is related to pharmaceutical presentation forms. There is no study showing xantan gum-based hydrogel and polycaprolactone nanoparticles containing A. satureioides extract against R. microplus larvae. The objective of this study was to incorporate A. satureioides extract to develop a nanoformulation (AScn) and a hydrogel (ASlh) and evaluate them against R. microplus larvae with the purpose of increasing the contact time of the extract with the larvae and improve the effectiveness. The ethanolic extracts were incorporated in polycaprolactone nanoparticles and characterized via analysis of the mean hydrodinamic diameter and polidispersity index. The xanthan gum-based hydrogel formulation was prepared with crude extract of A. satureioides 40 mg/mL, 0.25% xanthan gum, and 8% poloxamer, to determine the bioadhesiveness of the formulation in bovine leather and the flow rate of the formulation in the animal. The results in larvae demonstrated that when evaluated in the form of a hydrogel (ASlh), mortality was higher, with 91.48% mortality at a concentration of 20 mg/mL presenting itself as an interesting alternative for controlling this ectoparasite.
Keywords: Achyrocline satureioides; Rhipicephalus microplus; acaricidal activity; hydrogel; xanthan gum.
Conflict of interest statement
Ana Carolina de Souza Chagas was employed by EMBRAPA-Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Calvano M.P.C.A., Brumatti R.C., Barros J.C., Garcia M.V., Martins K.R., Andreotti R. Bioeconomic simulation of Rhipicephalus microplus infestation in different beef cattle production systems in the Brazilian Cerrado. Agric. Syst. 2021;194:103247. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2021.103247. - DOI
-
- Chagas A.C.S., Domingues L.F., Fantatto R.R., Giglioti R., Oliveira M.C.S., Oliveira D.H., Mano R.A., Jacob R.G. In vitro and in vivo acaricide action of juvenoid analogs produced from the chemical modification of Cymbopogon spp. and Corymbia citriodora essential oil on the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Vet. Parasitol. 2014;205:277–284. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2014.06.030. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Camargo B.A.F., Silva D.E.S., Silva A.N., Campos D.L., Ribeiro T.R.M., Mieli M.J., Zanatta M.B.T., Silva P.B., Pavan F.R., Moreira C.G., et al. A new silver (I) coordination compound loaded into polymeric nanoparticles as a strategy to improve in vitro anti-Helicobacter pylori activity. Mol. Pharm. 2020;17:2287–2298. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b01264. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

