Emotion Recognition Using EEG Signals and Audiovisual Features with Contrastive Learning
- PMID: 39451373
- PMCID: PMC11504283
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering11100997
Emotion Recognition Using EEG Signals and Audiovisual Features with Contrastive Learning
Abstract
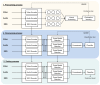
Multimodal emotion recognition has emerged as a promising approach to capture the complex nature of human emotions by integrating information from various sources such as physiological signals, visual behavioral cues, and audio-visual content. However, current methods often struggle with effectively processing redundant or conflicting information across modalities and may overlook implicit inter-modal correlations. To address these challenges, this paper presents a novel multimodal emotion recognition framework which integrates audio-visual features with viewers' EEG data to enhance emotion classification accuracy. The proposed approach employs modality-specific encoders to extract spatiotemporal features, which are then aligned through contrastive learning to capture inter-modal relationships. Additionally, cross-modal attention mechanisms are incorporated for effective feature fusion across modalities. The framework, comprising pre-training, fine-tuning, and testing phases, is evaluated on multiple datasets of emotional responses. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed multimodal approach, which combines audio-visual features with EEG data, is highly effective in recognizing emotions, highlighting its potential for advancing emotion recognition systems.
Keywords: contrastive learning; cross-attention mechanism; emotion recognition; multimodal learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Andalibi N., Buss J. The human in emotion recognition on social media: Attitudes, outcomes, risks; Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems; Honolulu, HI, USA. 25–30 April 2020; pp. 1–16.
-
- Dubey A., Shingala B., Panara J.R., Desai K., Sahana M. Digital Content Recommendation System through Facial Emotion Recognition. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023;11:1272–1276. doi: 10.22214/ijraset.2023.49225. - DOI
-
- Pepa L., Spalazzi L., Capecci M., Ceravolo M.G. Automatic emotion recognition in clinical scenario: A systematic review of methods. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2021;14:1675–1695. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2021.3128787. - DOI
-
- Caruelle D., Shams P., Gustafsson A., Lervik-Olsen L. Affective computing in marketing: Practical implications and research opportunities afforded by emotionally intelligent machines. Mark. Lett. 2022;33:163–169. doi: 10.1007/s11002-021-09609-0. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

