The Diagnostic Value of bpMRI in Prostate Cancer: Benefits and Limitations Compared to mpMRI
- PMID: 39451382
- PMCID: PMC11505328
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering11101006
The Diagnostic Value of bpMRI in Prostate Cancer: Benefits and Limitations Compared to mpMRI
Abstract
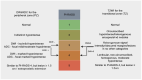
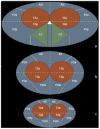
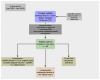
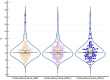
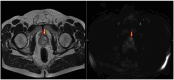
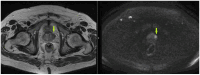
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men and a leading cause of death worldwide. Early detection is vital, as it often presents with vague symptoms such as nocturia and poor urinary stream. Diagnostic tools like PSA tests, ultrasound, PET-CT, and mpMRI are essential for prostate cancer management. The PI-RADS system helps assess malignancy risk based on imaging. While mpMRI, which includes T1, T2, DWI, and dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging (DCE), is the standard, bpMRI offers a contrast-free alternative using only T2 and DWI. This reduces costs, acquisition time, and the risk of contrast-related side effects but has limitations in detecting higher-risk PI-RADS 3 and 4 lesions. This study compared bpMRI's diagnostic accuracy to mpMRI, focusing on prostate volume and PI-RADS scoring. Both methods showed strong inter-rater agreement for prostate volume (ICC 0.9963), confirming bpMRI's reliability in this aspect. However, mpMRI detected more complex conditions, such as periprostatic fat infiltration and iliac lymphadenopathy, which bpMRI missed. While bpMRI offers advantages like reduced cost and no contrast use, it is less effective for higher-risk lesions, making mpMRI more comprehensive.
Keywords: bpMRI; mpMRI; prostate cancer diagnosis; prostate cancer imaging; prostate volume assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

