Advances in Medical Image Segmentation: A Comprehensive Review of Traditional, Deep Learning and Hybrid Approaches
- PMID: 39451409
- PMCID: PMC11505408
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering11101034
Advances in Medical Image Segmentation: A Comprehensive Review of Traditional, Deep Learning and Hybrid Approaches
Abstract
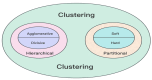
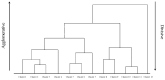
Medical image segmentation plays a critical role in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning, enabling precise analysis across a wide range of clinical tasks. This review begins by offering a comprehensive overview of traditional segmentation techniques, including thresholding, edge-based methods, region-based approaches, clustering, and graph-based segmentation. While these methods are computationally efficient and interpretable, they often face significant challenges when applied to complex, noisy, or variable medical images. The central focus of this review is the transformative impact of deep learning on medical image segmentation. We delve into prominent deep learning architectures such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Fully Convolutional Networks (FCNs), U-Net, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Adversarial Networks (GANs), and Autoencoders (AEs). Each architecture is analyzed in terms of its structural foundation and specific application to medical image segmentation, illustrating how these models have enhanced segmentation accuracy across various clinical contexts. Finally, the review examines the integration of deep learning with traditional segmentation methods, addressing the limitations of both approaches. These hybrid strategies offer improved segmentation performance, particularly in challenging scenarios involving weak edges, noise, or inconsistent intensities. By synthesizing recent advancements, this review provides a detailed resource for researchers and practitioners, offering valuable insights into the current landscape and future directions of medical image segmentation.
Keywords: biomedical engineering; deep learning; diagnostic imaging; image segmentation; medical image processing; medical imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

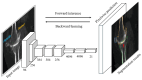
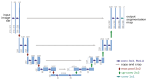
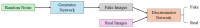
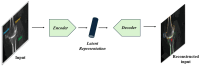
References
-
- Panayides A.S., Amini A., Filipovic N.D., Sharma A., Tsaftaris S.A., Young A., Foran D., Do N., Golemati S., Kurc T., et al. AI in Medical Imaging Informatics: Current Challenges and Future Directions. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020;24:1837–1857. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.2991043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdou M.A. Literature Review: Efficient Deep Neural Networks Techniques for Medical Image Analysis. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022;34:5791–5812. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-06960-9. - DOI
-
- Nyo M.T., Mebarek-Oudina F., Hlaing S.S., Khan N.A. Otsu’s Thresholding Technique for MRI Image Brain Tumor Segmentation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022;81:43837–43849. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-13215-1. - DOI
-
- Abdel-Gawad A.H., Said L.A., Radwan A.G. Optimized Edge Detection Technique for Brain Tumor Detection in MR Images. IEEE Access. 2020;8:136243–136259. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3009898. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

