Protective Effects of Cervus elaphus and Eucommia ulmoides Mixture (KGC01CE) on Muscle Loss and Function in Aged Rats
- PMID: 39451544
- PMCID: PMC11506417
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46100664
Protective Effects of Cervus elaphus and Eucommia ulmoides Mixture (KGC01CE) on Muscle Loss and Function in Aged Rats
Abstract
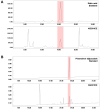
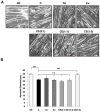
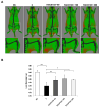
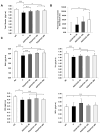
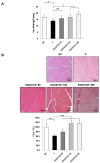
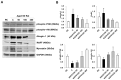
Sarcopenia is a condition characterized by a progressive loss of muscle mass and function which are influenced by certain factors such as aging, nutritional deficiencies, and chronic diseases. Despite numerous efforts to prevent or treat sarcopenia, effective therapeutic options for this disease remain limited. This study aims to evaluate the effects of KGC01CE treatment, a mixture of Cervus elaphus (Ce) and Eucommia ulmoides (Eu), which are well-known traditional herbal medicines in Asia, on age-related muscle loss and functional decline in aged rats. KGC01CE has been found to be more effective than the individual extracts in inhibiting dexamethasone (DEX)-induced muscle atrophy and improving muscle mass and grip strength in C2C12 cells and aged rats. Moreover, animal studies were conducted to determine the minimum effective dose, and a 12-week oral administration of KGC01CE treatment at doses of 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg to 15-month-old aged rats resulted in a dose-dependent increase in lean mass, muscle mass, grip strength, and muscle cross-sectional area (CSA), which had decreased due to aging. Furthermore, it was shown that KGC01CE activated the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway and inhibited the expression of muscle-degrading proteins MuRF, Atrogin-1, and myostatin. These results suggest that KGC01CE treatment may effectively prevent muscle loss and functional decline, providing a novel therapeutic strategy for sarcopenia.
Keywords: Cervus elaphus; Eucommia ulmoides; KGC01CE; muscle atrophy; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that this research was funded by Korea Ginseng Corporation. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results. The authors affirm that the research findings and manuscript content reflect their independent opinions and interpretations.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

