Blind Separation of Skin Chromophores from Multispectral Dermatological Images
- PMID: 39451611
- PMCID: PMC11506256
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14202288
Blind Separation of Skin Chromophores from Multispectral Dermatological Images
Abstract
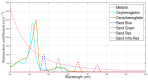
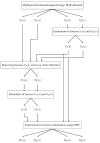
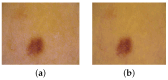
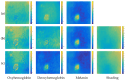
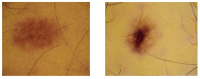
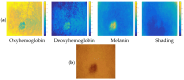
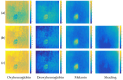
Background/Objectives: Based on Blind Source Separation and the use of multispectral imaging, the new approach we propose in this paper aims to improve the estimation of the concentrations of the main skin chromophores (melanin, oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin), while considering shading as a fully-fledged source. Methods: In this paper, we demonstrate that the use of the Infra-Red spectral band, in addition to the traditional RGB spectral bands of dermatological images, allows us to model the image provided by each spectral band as a mixture of the concentrations of the three chromophores in addition to that of the shading, which are estimated through four steps using Blind Source Separation. Results: We studied the performance of our new method on a database of real multispectral dermatological images of melanoma by proposing a new quantitative performances measurement criterion based on mutual information. We then validated these performances on a database of multispectral dermatological images that we simulated using our own new protocol. Conclusions: All the results obtained demonstrated the effectiveness of our new approach for estimating the concentrations of the skin chromophores from a multispectral dermatological image, compared to traditional approaches that consist of using only the RGB image by neglecting shading.
Keywords: Blind Source Separation; chromophores; deoxyhemoglobin; melanin; multispectral dermatological images; oxyhemoglobin; shading.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Three-dimensional representation of triple spectral line imaging data as an option for noncontact skin diagnostics.J Biomed Opt. 2022 Sep;27(9):095005. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.9.095005. J Biomed Opt. 2022. PMID: 36114603 Free PMC article.
-
Blind source separation of ex-vivo aorta tissue multispectral images.Biomed Opt Express. 2015 Apr 6;6(5):1589-98. doi: 10.1364/BOE.6.001589. eCollection 2015 May 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2015. PMID: 26137366 Free PMC article.
-
An Analytical Study on the Utility of RGB and Multispectral Imagery with Band Selection for Automated Tumor Grading.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jul 27;14(15):1625. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14151625. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39125501 Free PMC article.
-
Skin chromophore mapping by smartphone RGB camera under spectral band and spectral line illumination.J Biomed Opt. 2022 Feb;27(2):026004. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.2.026004. J Biomed Opt. 2022. PMID: 35191236 Free PMC article.
-
Multispectral Imaging for Skin Diseases Assessment-State of the Art and Perspectives.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Apr 11;23(8):3888. doi: 10.3390/s23083888. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37112229 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson R., Parrish J. The Science of Photomedicine. Springer; Boston, MA, USA: 1982. Optical Properties of Human Skin.
-
- Zokay M., Saylani H. A new approach for identifying skin diseases from dermatological RGB images using source separation; Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Medical Image Understanding and Analysis; Aberdeen, UK. 19–21 July 2023; pp. 242–256. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

