Image Quality and Lesion Detectability of Low-Concentration Iodine Contrast and Low Radiation Hepatic Multiphase CT Using a Deep-Learning-Based Contrast-Boosting Model in Chronic Liver Disease Patients
- PMID: 39451631
- PMCID: PMC11507254
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14202308
Image Quality and Lesion Detectability of Low-Concentration Iodine Contrast and Low Radiation Hepatic Multiphase CT Using a Deep-Learning-Based Contrast-Boosting Model in Chronic Liver Disease Patients
Abstract
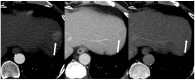
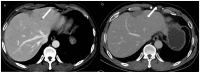
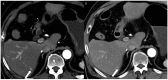
Background: This study investigated the image quality and detectability of double low-dose hepatic multiphase CT (DLDCT, which targeted about 30% reductions of both the radiation and iodine concentration) using a vendor-agnostic deep-learning-based contrast-boosting model (DL-CB) compared to those of standard-dose CT (SDCT) using hybrid iterative reconstruction.
Methods: The CT images of 73 patients with chronic liver disease who underwent DLDCT between June 2023 and October 2023 and had SDCT were analyzed. Qualitative analysis of the overall image quality, artificial sensation, and liver contour sharpness on the arterial and portal phase, along with the hepatic artery clarity was conducted by two radiologists using a 5-point scale. For quantitative analysis, the image noise, signal-to-noise ratio, and contrast-to-noise ratio were measured. The lesion conspicuity was analyzed using generalized estimating equation analysis. Lesion detection was evaluated using the jackknife free-response receiver operating characteristic figures-of-merit.
Results: Compared with SDCT, a significantly lower effective dose (16.4 ± 7.2 mSv vs. 10.4 ± 6.0 mSv, 36.6% reduction) and iodine amount (350 mg iodine/mL vs. 270 mg iodine/mL, 22.9% reduction) were utilized in DLDCT. The mean overall arterial and portal phase image quality scores of DLDCT were significantly higher than SDCT (arterial phase, 4.77 ± 0.45 vs. 4.93 ± 0.24, AUCVGA 0.572 [95% CI, 0.507-0.638]; portal phase, 4.83 ± 0.38 vs. 4.92 ± 0.26, AUCVGA 0.535 [95% CI, 0.469-0.601]). Furthermore, DLDCT showed significantly superior quantitative results for the lesion contrast-to-noise ratio (7.55 ± 4.55 vs. 3.70 ± 2.64, p < 0.001) and lesion detectability (0.97 vs. 0.86, p = 0.003).
Conclusions: In patients with chronic liver disease, DLDCT using DL-CB can provide acceptable image quality without impairing the detection and evaluation of hepatic focal lesions compared to SDCT.
Keywords: deep learning; image reconstruction; low iodine concentration; multidetector computed tomography; radiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Chulwoo Park was employed by the company Siemens Healthineers Ltd. All authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Chhikara B.S., Parang K. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: The trends projection analysis. Chem. Biol. Lett. 2023;10:451
-
- Chernyak V., Fowler K.J., Kamaya A., Kielar A.Z., Elsayes K.M., Bashir M.R., Kono Y., Do R.K., Mitchell D.G., Singal A.G., et al. Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS) Version 2018: Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in At-Risk Patients. Radiology. 2018;289:816–830. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018181494. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

