Tear-Based Ocular Wearable Biosensors for Human Health Monitoring
- PMID: 39451696
- PMCID: PMC11506517
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14100483
Tear-Based Ocular Wearable Biosensors for Human Health Monitoring
Abstract
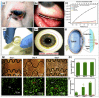
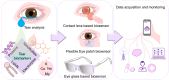
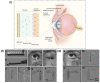
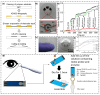
Wearable tear-based biosensors have garnered substantial interest for real time monitoring with an emphasis on personalized health care. These biosensors utilize major tear biomarkers such as proteins, lipids, metabolites, and electrolytes for the detection and recording of stable biological signals in a non-invasive manner. The present comprehensive review delves deep into the tear composition along with potential biomarkers that can identify, monitor, and predict certain ocular diseases such as dry eye disease, conjunctivitis, eye-related infections, as well as diabetes mellitus. Recent technologies in tear-based wearable point-of-care medical devices, specifically the state-of-the-art and prospects of glucose, pH, lactate, protein, lipid, and electrolyte sensing from tear are discussed. Finally, the review addresses the existing challenges associated with the widespread application of tear-based sensors, which will pave the way for advanced scientific research and development of such non-invasive health monitoring devices.
Keywords: biomarkers; biosensors; healthcare; ocular; tear; wearable.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lab on the eye: A review of tear-based wearable devices for medical use and health management.Biosci Trends. 2019;13(4):308-313. doi: 10.5582/bst.2019.01178. Biosci Trends. 2019. PMID: 31527328 Review.
-
Eyeglasses-based tear biosensing system: Non-invasive detection of alcohol, vitamins and glucose.Biosens Bioelectron. 2019 Jul 15;137:161-170. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.04.058. Epub 2019 May 7. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019. PMID: 31096082 Free PMC article.
-
Achievements and Challenges for Real-Time Sensing of Analytes in Sweat within Wearable Platforms.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Feb 19;52(2):297-306. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00555. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 30688433 Review.
-
Contact-Lens Biosensors.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Aug 13;18(8):2651. doi: 10.3390/s18082651. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30104496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wearable biosensors in cardiovascular disease.Clin Chim Acta. 2024 Jul 15;561:119766. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2024.119766. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Clin Chim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38857672 Review.
Cited by
-
Bionic Sensors for Biometric Acquisition and Monitoring: Challenges and Opportunities.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jun 26;25(13):3981. doi: 10.3390/s25133981. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40648236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing glaucoma care with smart contact lenses: An overview of recent developments.Biomed Microdevices. 2025 Apr 21;27(2):18. doi: 10.1007/s10544-025-00740-7. Biomed Microdevices. 2025. PMID: 40257617 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhu P., Peng H., Rwei A.Y. Flexible, wearable biosensors for digital health. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices. 2022;14:100118. doi: 10.1016/j.medntd.2022.100118. - DOI
-
- Roy K., Ghosh S.K., Sultana A., Garain S., Xie M., Bowen C.R., Henkel K., Schmeiβer D., Mandal D. A Self-Powered Wearable Pressure Sensor and Pyroelectric Breathing Sensor Based on GO Interfaced PVDF Nanofibers. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019;2:2013–2025. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.9b00033. - DOI
-
- Promphet N., Hinestroza J.P., Rattanawaleedirojn P., Soatthiyanon N., Siralertmukul K., Potiyaraj P., Rodthongkum N. Cotton thread-based wearable sensor for non-invasive simultaneous diagnosis of diabetes and kidney failure. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020;321:128549. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.128549. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

