Highly Sensitive Molecular Diagnostic Platform for Scrub Typhus Diagnosis Using O. tsutsugamushi Enrichment and Nucleic Acid Extraction
- PMID: 39451706
- PMCID: PMC11505917
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14100493
Highly Sensitive Molecular Diagnostic Platform for Scrub Typhus Diagnosis Using O. tsutsugamushi Enrichment and Nucleic Acid Extraction
Abstract
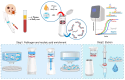
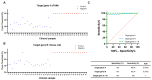
Scrub typhus is caused by the Gram-negative obligate intracellular bacterium Orientia tsutsugamushi, and this tick-borne disease is difficult to distinguish from other acute febrile illnesses as it typically presents with symptoms such as rash, crusting at the bite site, headache, myalgia, lymphadenopathy, and elevated liver transaminases. It can often be diagnosed clinically, but not all patients present with characteristic symptoms, so serological diagnosis and molecular techniques may be required. However, existing diagnostic tests often have low sensitivity and specificity, making early detection difficult. This study presents a nucleic acid extraction method using large volumes of plasma and buffy coat to increase sensitivity, as well as an improved detection method using two target genes. Using the I-PULL device, nucleic acids can be extracted from up to 4 mL of sample in 30 min, avoiding contamination. The extracted DNA detects two genes of O. tsutsugamushi, increasing sensitivity compared to single-gene detection. Clinical validation in 38 patient samples showed 100% specificity and 95.24% sensitivity for the single target gene, with specificity and sensitivity rising to 100% when both genes are analyzed. This molecular diagnostic platform can be useful for distinguishing scrub typhus from similar diseases.
Keywords: DNA detection kit; molecular diagnostics; sample preparation; scrub typhus.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Juho Jang, Jinkwan Lee, Namheon Kim were employed by the company INFUSIONTECH. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kim S., Kim A.R., Lim S., Lee S.J., Bae M. Real-world utility of serological tests in patients with suspected scrub typhus in the Republic of Korea: A single-center, retrospective, observational study. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2024;17:273–280. doi: 10.4103/apjtm.apjtm_815_23. - DOI
-
- Leelarasamee A., Chupaprawan C., Chenchittikul M., Udompanthurat S. Etiologies of acute undifferentiated febrile illness in Thailand. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2004;87:464–472. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

