Recent Advancements in MXene-Based Biosensors for Health and Environmental Applications-A Review
- PMID: 39451710
- PMCID: PMC11506004
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14100497
Recent Advancements in MXene-Based Biosensors for Health and Environmental Applications-A Review
Abstract
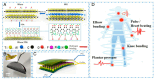
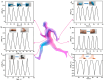
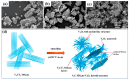
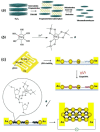
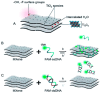
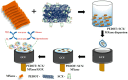
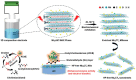
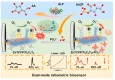
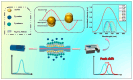
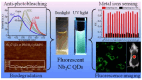
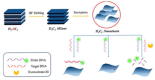
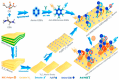
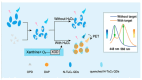
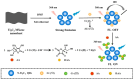
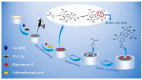
Owing to their unique physicochemical properties, MXenes have emerged as promising materials for biosensing applications. This review paper comprehensively explores the recent advancements in MXene-based biosensors for health and environmental applications. This review begins with an introduction to MXenes and biosensors, outlining various types of biosensors including electrochemical, enzymatic, optical, and fluorescent-based systems. The synthesis methods and characteristics of MXenes are thoroughly discussed, highlighting the importance of these processes in tailoring MXenes for specific biosensing applications. Particular attention is given to the development of electrochemical MXene-based biosensors, which have shown remarkable sensitivity and selectivity in detecting various analytes. This review then delves into enzymatic MXene-based biosensors, exploring how the integration of MXenes with enzymes enhances sensor performance and expands the range of detectable biomarkers. Optical biosensors based on MXenes are examined, focusing on their mechanisms and applications in both healthcare and environmental monitoring. The potential of fluorescent-based MXene biosensors is also investigated, showcasing their utility in imaging and sensing applications. In addition, MXene-based potential wearable biosensors have been discussed along with the role of MXenes in volatile organic compound (VOC) detection for environmental applications. Finally, this paper concludes with a critical analysis of the current state of MXene-based biosensors and provides insights into future perspectives and challenges in this rapidly evolving field.
Keywords: MXene; MXene-based biosensors; MXene/MOF composite-based biosensors; fluorescence-based biosensors; optical biosensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Philip A., Kumar A.R. Two-dimensional materials and their role in sensitivity enhancement of surface plasmon resonancebased biosensor. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024;171:117497–117524. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2023.117497. - DOI
-
- Thenmozhi R., Maruthasalamoorthy S., Nirmala R., Navamathavan R. Review—MXene Based Transducer for Biosensor Applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021;168:117507–117532. doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/ac2fc6. - DOI
-
- Sunkari D., Deshmukh K., Panda S., Pasha S.K.K. Recent progress in MXene-based materials for lithium-ion and lithium-sulphur batteries: A comprehensive review. J. Energy Storage. 2024;92:112017. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2024.112017. - DOI
-
- Pisani F., Zaheer A., Babar Z.U.D., Velotta R., Granata C., Tessicini F., Ventura B.D., Iannotti V. Unveiling Biosensing Innovations: Laser Scattering Sensor and Gold Nanoparticles-Decorated Ti3C2 MXene Composite for Enhanced Biosensing Applications. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2024;8:1501204. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2024.3407530. - DOI
-
- Roy S., Mondol N., Kundu D., Meem A.A., Islam M.R., Hossain M.A., Hossain M.B. Numerical investigation into impact of halide perovskite material on the optical performance of prism-loaded hybrid surface plasmon resonance biosensor: A strategy to increase sensitivity. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2024;43:100630. doi: 10.1016/j.sbsr.2024.100630. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

