Progression in Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Technology for Lung Cancer Management
- PMID: 39451714
- PMCID: PMC11506746
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14100501
Progression in Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Technology for Lung Cancer Management
Abstract
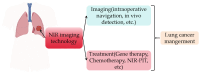
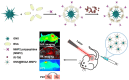
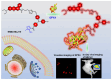
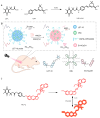
Lung cancer is a major threat to human health and a leading cause of death. Accurate localization of tumors in vivo is crucial for subsequent treatment. In recent years, fluorescent imaging technology has become a focal point in tumor diagnosis and treatment due to its high sensitivity, strong selectivity, non-invasiveness, and multifunctionality. Molecular probes-based fluorescent imaging not only enables real-time in vivo imaging through fluorescence signals but also integrates therapeutic functions, drug screening, and efficacy monitoring to facilitate comprehensive diagnosis and treatment. Among them, near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence imaging is particularly prominent due to its improved in vivo imaging effect. This trend toward multifunctionality is a significant aspect of the future advancement of fluorescent imaging technology. In the past years, great progress has been made in the field of NIR fluorescence imaging for lung cancer management, as well as the emergence of new problems and challenges. This paper generally summarizes the application of NIR fluorescence imaging technology in these areas in the past five years, including the design, detection principles, and clinical applications, with the aim of advancing more efficient NIR fluorescence imaging technologies to enhance the accuracy of tumor diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: diagnosis; in vivo imaging; lung cancer; near-infrared fluorescence; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

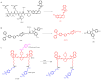


Similar articles
-
Recent Advances in Near-Infrared-II Fluorescence Imaging for Deep-Tissue Molecular Analysis and Cancer Diagnosis.Small. 2022 Aug;18(31):e2202035. doi: 10.1002/smll.202202035. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Small. 2022. PMID: 35762403 Review.
-
The multifaceted roles of peptides in "always-on" near-infrared fluorescent probes for tumor imaging.Bioorg Chem. 2022 Dec;129:106182. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106182. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Bioorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 36341739 Review.
-
Recent Progress in Second Near-Infrared (NIR-II) Fluorescence Imaging in Cancer.Biomolecules. 2022 Jul 28;12(8):1044. doi: 10.3390/biom12081044. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36008937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging for In Vivo Quantitative Analysis.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Jun 5;16(22):28011-28028. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c04913. Epub 2024 May 23. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38783516 Review.
-
Intraoperative near-infrared fluorescence imaging targeting folate receptors identifies lung cancer in a large-animal model.Cancer. 2017 May 15;123(6):1051-1060. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30419. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28263385 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Enhancing Glioblastoma Resection with NIR Fluorescence Imaging: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 27;16(23):3984. doi: 10.3390/cancers16233984. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2023JJ60039/National Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- B202303027655/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province National Health Commission
- Kq2208150/Natural Science Foundation of Changsha Science and Technology Bureau
- 320.6750.2022-22-59/Wu Jieping Foundation of China
- 320.6750.2022-17-41/Wu Jieping Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

