Intelligent Evaluation and Dynamic Prediction of Oysters Freshness with Electronic Nose Non-Destructive Monitoring and Machine Learning
- PMID: 39451715
- PMCID: PMC11506465
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14100502
Intelligent Evaluation and Dynamic Prediction of Oysters Freshness with Electronic Nose Non-Destructive Monitoring and Machine Learning
Abstract
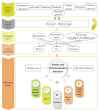
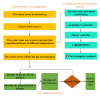
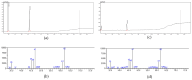
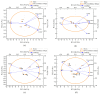
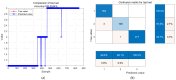
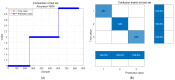
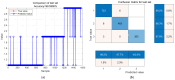
Physiological and environmental fluctuations in the oyster cold chain can lead to quality deterioration, highlighting the importance of monitoring and evaluating oyster freshness. In this study, an electronic nose was developed using ten partially selective metal oxide-based gas sensors for rapid freshness assessment. Simultaneous analyses, including GC-MS, TVBN, microorganism, texture, and sensory evaluations, were conducted to assess the quality status of oysters. Real-time electronic nose measurements were taken at various storage temperatures (4 °C, 12 °C, 20 °C, 28 °C) to thoroughly investigate quality changes under different storage conditions. Principal component analysis was utilized to reduce the 10-dimensional vectors to 3-dimensional vectors, enabling the clustering of samples into fresh, sub-fresh, and decayed categories. A GA-BP neural network model based on these three classes achieved a test data accuracy rate exceeding 93%. Expert input was solicited for performance analysis and optimization suggestions enhanced the efficiency and applicability of the established prediction system. The results demonstrate that combining an electronic nose with quality indices is an effective approach for diagnosing oyster spoilage and mitigating quality and safety risks in the oyster industry.
Keywords: GA-BP; electronic nose; gas sensor; intelligent evaluation; non-destructive monitoring; oyster freshness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
Figures








References
-
- Wright A.C., Fan Y., Baker G.L. Nutritional value and food safety of bivalve molluscan shellfish. J. Shellfish Res. 2018;37:695–708. doi: 10.2983/035.037.0403. - DOI
-
- Pérez-Mateos M., López-Caballero M.E., Montero P. Effect of High Pressure and 4-Hexylresorcinol on Enzymatic Activity and Darkening in Oysters. J. Food Sci. 2002;67:2107–2112. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2002.tb09509.x. - DOI
-
- Dong S., Niu Y., Wei H., Lin Y., Lu X., Yamashita T., Yu K., Takaki K., Yuan C. Effect of super-chilling storage on maintenance of quality and freshness of the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) Food Qual. Saf. 2023;7:fyad008. doi: 10.1093/fqsafe/fyad008. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

