Bazedoxifene as a Potential Cancer Therapeutic Agent Targeting IL-6/GP130 Signaling
- PMID: 39451730
- PMCID: PMC11505662
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol31100426
Bazedoxifene as a Potential Cancer Therapeutic Agent Targeting IL-6/GP130 Signaling
Abstract
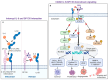
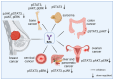
Targeting the interleukin-6 (IL-6)/glycoprotein 130 (GP130) signaling pathway holds significant promise for cancer therapy given its essential role in the survival and progression of various cancer types. We have identified that bazedoxifene (BZA), a Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drug used for the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis, when combined with conjugated estrogens in Duavee, also has a novel function as an inhibitor of IL-6/GP130 interaction. BZA is currently under investigation for its potential anticancer therapeutic function through the inhibition of the IL-6/GP130 pathway. Numerous studies have highlighted the efficacy of BZA (monotherapy or combined with other chemotherapy drugs) in impeding progression across multiple cancers. In this review, we mainly focus on the anticancer activity of BZA and the underlying anticancer mechanism through inhibition of the IL-6/GP130 pathway, aiming to provide valuable insights for the design and execution of further research and the potential repositioning of BZA in oncological clinical trials.
Keywords: Bazedoxifene; GP130; IL-6; STAT3; cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

