Searching for New Biomarkers of Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Comparative Analysis of Chromogranin A and Inflammatory Cytokines in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors
- PMID: 39451760
- PMCID: PMC11506232
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol31100456
Searching for New Biomarkers of Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Comparative Analysis of Chromogranin A and Inflammatory Cytokines in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors
Abstract
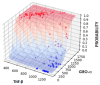
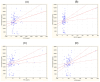
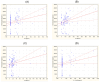
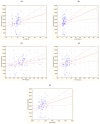
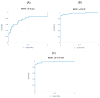
Neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs) present a diagnostic challenge due to their heterogeneous nature and non-specific clinical manifestations. This study aimed to explore novel biomarkers for NENs. Serum chromogranin A (CgA) levels and a panel of 48 inflammatory cytokines were analyzed in a cohort of 84 NEN patients and 40 healthy controls using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and multiplex ELISA. Significant alterations in cytokine levels were observed in the NEN patients compared to the controls, including elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and reduced levels of angiogenic factors like platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) and tumor necrosis factor beta (TNF-β). Notably, cytokines such as growth-regulated alpha protein (GRO-α) and TNF-β demonstrated strong potential as diagnostic markers, with receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses showing high sensitivity and specificity. Additionally, a positive correlation was found between CgA levels and several inflammatory cytokines, suggesting their synergistic role in tumor progression. These findings highlight the limited reliability of CgA alone as a diagnostic marker and underscore the importance of a multi-marker approach in diagnosing and monitoring NENs. Further research on a larger cohort is necessary to validate these biomarkers and their potential clinical applications.
Keywords: cancer; chromogranin A; cytokines; diagnostic markers; neuroendocrine tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Trofimiuk-Müldner M., Lewkowicz E., Wysocka K., Pach D., Kiełtyka A., Stefańska A., Sowa-Staszczak A., Tomaszewska R., Hubalewska-Dydejczyk A. Epidemiology of Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms in Krakow and Krakow District in 2007–2011. Endokrynol. Pol. 2017;68:42–46. doi: 10.5603/EP.2017.0006. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

