Pose Estimation of a Cobot Implemented on a Small AI-Powered Computing System and a Stereo Camera for Precision Evaluation
- PMID: 39451816
- PMCID: PMC11505535
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics9100610
Pose Estimation of a Cobot Implemented on a Small AI-Powered Computing System and a Stereo Camera for Precision Evaluation
Abstract
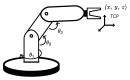
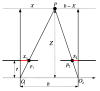
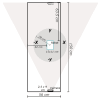
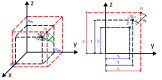
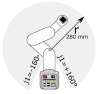
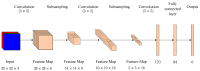
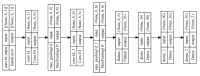
The precision of robotic manipulators in the industrial or medical field is very important, especially when it comes to repetitive or exhaustive tasks. Geometric deformations are the most common in this field. For this reason, new robotic vision techniques have been proposed, including 3D methods that made it possible to determine the geometric distances between the parts of a robotic manipulator. The aim of this work is to measure the angular position of a robotic arm with six degrees of freedom. For this purpose, a stereo camera and a convolutional neural network algorithm are used to reduce the degradation of precision caused by geometric errors. This method is not intended to replace encoders, but to enhance accuracy by compensating for degradation through an intelligent visual measurement system. The camera is tested and the accuracy is about one millimeter. The implementation of this method leads to better results than traditional and simple neural network methods.
Keywords: 3D vision; convolutional neural network; precision degradation; robot arm; robotic vision; stereo camera.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








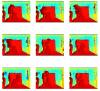
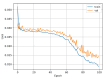


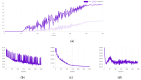


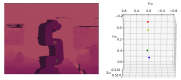
Similar articles
-
Implementation of six degree-of-freedom high-precision robotic phantom on commercial industrial robotic manipulator.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2021 Aug 9;7(5). doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/ac1988. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2021. PMID: 34330110
-
Detection, segmentation, and 3D pose estimation of surgical tools using convolutional neural networks and algebraic geometry.Med Image Anal. 2021 May;70:101994. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2021.101994. Epub 2021 Feb 7. Med Image Anal. 2021. PMID: 33611053
-
Intelligent Spacecraft Visual GNC Architecture With the State-Of-the-Art AI Components for On-Orbit Manipulation.Front Robot AI. 2021 Jun 1;8:639327. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2021.639327. eCollection 2021. Front Robot AI. 2021. PMID: 34141728 Free PMC article.
-
Monocular-Based 6-Degree of Freedom Pose Estimation Technology for Robotic Intelligent Grasping Systems.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Feb 14;17(2):334. doi: 10.3390/s17020334. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28216555 Free PMC article.
-
A Manufacturing-Oriented Intelligent Vision System Based on Deep Neural Network for Object Recognition and 6D Pose Estimation.Front Neurorobot. 2021 Jan 7;14:616775. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2020.616775. eCollection 2020. Front Neurorobot. 2021. PMID: 33488378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kelly R., Santibáñez V. Control de Movimiento de Robots Manipuladores. Pearson Educación; London, UK: 2003.
-
- Qiao G., Weiss B. Industrial robot accuracy degradation monitoring and quick health assessment. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2019;141:071006. doi: 10.1115/1.4043649. - DOI
-
- Zhang D., Peng Z., Ning G., Han X. Positioning accuracy reliability of industrial robots through probability and evidence theories. J. Mech. Des. 2021;143:011704. doi: 10.1115/1.4047436. - DOI
-
- Wang Z., Liu R., Sparks T., Chen X., Liou F. Industrial Robot Trajectory Accuracy Evaluation Maps for Hybrid Manufacturing Process Based on Joint Angle Error Analysis. OMICS International; Hyderabad, India: 2018.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

