Bionic Multi-Legged Robots with Flexible Bodies: Design, Motion, and Control
- PMID: 39451834
- PMCID: PMC11506302
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics9100628
Bionic Multi-Legged Robots with Flexible Bodies: Design, Motion, and Control
Abstract
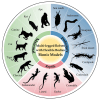
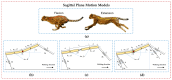
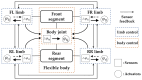
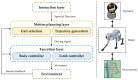
Bionic multi-legged robots with flexible bodies embody human ingenuity in imitating, learning, and exploring the natural world. In contrast to rigid-body robots, these robots with flexible bodies exhibit superior locomotive capabilities. The flexible body of the robot not only boosts the moving speed and walking stability but also enhances adaptability across complex terrains. This article focuses on the innovative design of flexible bodies. Firstly, the structural designs, including artificial spines and single/multi-axis articulation mechanisms, are outlined systematically. Secondly, the enhancement of robotic motion by flexible bodies is reviewed, examining the impact that body degrees of freedom, stiffness, and coordinated control between the body and limbs have on robotic motion. Thirdly, existing robotic control methods, organized by control architectures, are comprehensively overviewed in this article. Finally, the application prospects of bionic multi-legged robots with flexible bodies are offered, and the challenges that may arise in their future development are listed. This article aims to serve as a reference for bionic robot research.
Keywords: CPG; bionic control; bionic robots; flexible body; locomotion; multi-legged robots; spine.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Dan Liu was employed by the company Inner Mongolia First Machinery Group Co., Ltd, and author Wenqing Tian was employed by the company China FAW Group Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







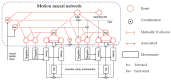
References
-
- Seok S., Wang A., Chuah M.Y., Otten D., Lang J., Kim S. Design Principles for Highly Efficient Quadrupeds and Implementation on the MIT Cheetah Robot; Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation; Karlsruhe, Germany. 6–10 May 2013; pp. 3307–3312.
-
- Park S., Lee Y.-J. Discontinuous Zigzag Gait Planning of a Quadruped Walking Robot with a Waist-Joint. Adv. Robot. 2007;21:143–164. doi: 10.1163/156855307779293733. - DOI
-
- Park S.H., Kim D.S., Lee Y.J. Discontinuous Spinning Gait of a Quadruped Walking Robot with Waist-Joint; Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems; Edmonton, AB, Canada. 2–6 August 2005; pp. 2744–2749.
-
- Tang Z., Qi P., Dai J. Mechanism Design of a Biomimetic Quadruped Robot. Ind. Robot. 2017;44:512–520. doi: 10.1108/IR-11-2016-0310. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

