Information Bottleneck Driven Deep Video Compression-IBOpenDVCW
- PMID: 39451913
- PMCID: PMC11507002
- DOI: 10.3390/e26100836
Information Bottleneck Driven Deep Video Compression-IBOpenDVCW
Abstract
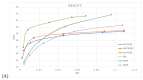
Video compression remains a challenging task despite significant advancements in end-to-end optimized deep networks for video coding. This study, inspired by information bottleneck (IB) theory, introduces a novel approach that combines IB theory with wavelet transform. We perform a comprehensive analysis of information and mutual information across various mother wavelets and decomposition levels. Additionally, we replace the conventional average pooling layers with a discrete wavelet transform creating more advanced pooling methods to investigate their effects on information and mutual information. Our results demonstrate that the proposed model and training technique outperform existing state-of-the-art video compression methods, delivering competitive rate-distortion performance compared to the AVC/H.264 and HEVC/H.265 codecs.
Keywords: deep video compression; information bottleneck; neural networks; wavelets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Symes P. Digital Video Compression. McGraw-Hill; New York, NY, USA: 2004. (Digital Video/Audio Series).
-
- Zhang Z., Shi Y., Toda H., Akiduki T. A Study of a new wavelet neural network for deep learning; Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Wavelet Analysis and Pattern Recognition (ICWAPR); Ningbo, China. 9–12 July 2017; pp. 127–131. - DOI
-
- Ma S., Zhang X., Jia C., Zhao Z., Wang S., Wang S. Image and Video Compression with Neural Networks: A Review. arXiv. 2019 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2910119.1904.03567 - DOI
-
- Shin S. Industrial application of wavelet analysis; Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Wavelet Analysis and Pattern Recognition; Hong Kong, China. 30–31 August 2008; pp. 607–610. - DOI
-
- Keinert F. Wavelets and Multiwavelets. Studies in Advanced Mathematics; CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2003.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

