Effects of Cannabidiol (CBD) on Doxorubicin-Induced Anxiety and Depression-like Behaviors and mRNA Expression of Inflammatory Markers in Rats
- PMID: 39452013
- PMCID: PMC11505750
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci14100999
Effects of Cannabidiol (CBD) on Doxorubicin-Induced Anxiety and Depression-like Behaviors and mRNA Expression of Inflammatory Markers in Rats
Abstract
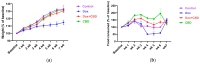
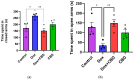
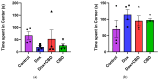
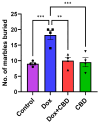
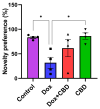
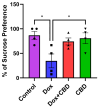
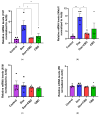
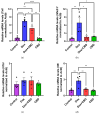
Background: Post-treatment side effects of chemotherapy can include cognitive deficits commonly known as Chemo-brain. The treatment of patients with Doxorubicin (DOX), one of the most widely used chemotherapeutic drugs in the treatment of cancer, can induce depression, anxiety, and impaired cognitive function. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive component of Cannabis sativa that has been identified as a possible therapeutic agent against many neurodegenerative disorders, including traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury, Tau-protein-induced neurodegeneration, and neuropathic pain. Therefore, this study aimed to assess whether oral CBD administration could reduce DOX-induced anxiety and depression-like behaviors and alter the expression of mRNA associated with neuroinflammation. Methods: Female Long Evans Hooded rats received intraperitoneal injections of DOX (6 mg/kg) or the vehicle (0.9% saline) once a week for four weeks, followed by oral administration of CBD (10 mg/kg) three times a week for the same period. Results: CBD was significantly protective against DOX-induced anxiety and depression-like behaviors, as measured by several behavioral tests. Furthermore, CBD improved DOX-induced alterations in the gene expression of biomarkers of neuroinflammation in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Conclusions: This provides insights into future studies on possible mechanisms by which DOX-induced cognitive dysfunction could be alleviated by CBD.
Keywords: cannabidiol; chemo-brain; cognitive deficits; doxorubicin; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cannabidiol improves behavioural and neurochemical deficits in adult female offspring of the maternal immune activation (poly I:C) model of neurodevelopmental disorders.Brain Behav Immun. 2019 Oct;81:574-587. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.07.018. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Brain Behav Immun. 2019. PMID: 31326506
-
Cannabidiol ameliorates PTSD-like symptoms by inhibiting neuroinflammation through its action on CB2 receptors in the brain of male mice.Brain Behav Immun. 2024 Jul;119:945-964. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2024.05.016. Epub 2024 May 15. Brain Behav Immun. 2024. PMID: 38759736
-
Cannabidiol attenuates cognitive deficits and neuroinflammation induced by early alcohol exposure in a mice model.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Sep;141:111813. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111813. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34126352
-
Cannabidiol and brain function: current knowledge and future perspectives.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 15;14:1328885. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1328885. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38288087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and Preclinical Evidence for Functional Interactions of Cannabidiol and Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Jan;43(1):142-154. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.209. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28875990 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Argyriou A.A., Assimakopoulos K., Iconomou G., Giannakopoulou F., Kalofonos H.P. Either called “chemobrain” or “chemofog”, the long-term chemotherapy-induced cognitive decline in cancer survivors is real. J. Pain. Symptom Manage. 2011;41:126–139. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2010.04.021. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

