Strategic Integration: A Cross-Disciplinary Review of the fNIRS-EEG Dual-Modality Imaging System for Delivering Multimodal Neuroimaging to Applications
- PMID: 39452034
- PMCID: PMC11506513
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci14101022
Strategic Integration: A Cross-Disciplinary Review of the fNIRS-EEG Dual-Modality Imaging System for Delivering Multimodal Neuroimaging to Applications
Abstract
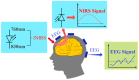
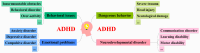
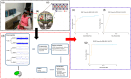
Background: Recent years have seen a surge of interest in dual-modality imaging systems that integrate functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) and electroencephalography (EEG) to probe brain function. This review aims to explore the advancements and clinical applications of this technology, emphasizing the synergistic integration of fNIRS and EEG. Methods: The review begins with a detailed examination of the fundamental principles and distinctive features of fNIRS and EEG techniques. It includes critical technical specifications, data-processing methodologies, and analysis techniques, alongside an exhaustive evaluation of 30 seminal studies that highlight the strengths and weaknesses of the fNIRS-EEG bimodal system. Results: The paper presents multiple case studies across various clinical domains-such as attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, infantile spasms, depth of anesthesia, intelligence quotient estimation, and epilepsy-demonstrating the fNIRS-EEG system's potential in uncovering disease mechanisms, evaluating treatment efficacy, and providing precise diagnostic options. Noteworthy research findings and pivotal breakthroughs further reinforce the developmental trajectory of this interdisciplinary field. Conclusions: The review addresses challenges and anticipates future directions for the fNIRS-EEG dual-modal imaging system, including improvements in hardware and software, enhanced system performance, cost reduction, real-time monitoring capabilities, and broader clinical applications. It offers researchers a comprehensive understanding of the field, highlighting the potential applications of fNIRS-EEG systems in neuroscience and clinical medicine.
Keywords: EEG; clinical application; dual-mode monitoring; fNIRS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Liu Z.M., Shore J., Wang M., Yuan F.P., Buss A., Zhao X.P. A systematic review on hybrid EEG/fNIRS in brain-computer interface. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2021;68:8. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102595. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

