Analyzing Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria from Wastewater in Pakistan Using Whole-Genome Sequencing
- PMID: 39452204
- PMCID: PMC11504851
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13100937
Analyzing Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria from Wastewater in Pakistan Using Whole-Genome Sequencing
Abstract
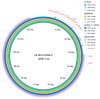
Background: Wastewater is a major source of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria (ARB) and a hotspot for the exchange of Antibiotic-Resistant Genes (ARGs). The occurrence of Carbapenem-Resistant Bacteria (CRB) in wastewater samples is a major public health concern. Objectives: This study aimed to analyze Antibiotic resistance in bacteria from wastewater sources in Pakistan. Methods: We analyzed 32 bacterial isolates, including 18 Escherichia coli, 4 Klebsiella pneumoniae, and 10 other bacterial isolates using phenotypic antibiotic susceptibility assay and whole-genome sequencing. This study identified the ARGs, plasmid replicons, and integron genes cassettes in the sequenced isolates. One representative isolate was further sequenced using Illumina and Oxford nanopore sequencing technologies. Results: Our findings revealed high resistance to clinically important antibiotics: 91% of isolates were resistant to cefotaxime, 75% to ciprofloxacin, and 62.5% to imipenem, while 31% showed non-susceptibility to gentamicin. All E. coli isolates were resistant to cephalosporins, with 72% also resistant to carbapenems. Sequence analysis showed a diverse resistome, including carbapenamases (blaNDM-5, blaOXA-181), ESBLs (blaCTX-M-15, blaTEM), and AmpC-type β-lactamases (blaCMY). Key point mutations noticed in the isolates were pmrB_Y358N (colistin) and ftsI_N337NYRIN, ftsI_I336IKYRI (carbapenem). The E. coli isolates had 11 different STs, with ST410 predominating (28%). Notably, the E. coli phylogroup A isolate 45EC1, (ST10886) is reported for the first time from wastewater, carrying blaNDM-5, blaCMY-16, and pmrB_Y358N with class 1 integron gene cassette of dfrA12-aadA2-qacEΔ1 on a plasmid-borne contig. Other carbapenamase, blaNDM-1 and blaOXA-72, were detected in K. pneumoniae 22EB1 and Acinetobacter baumannii 51AC1, respectively. The integrons with the gene cassettes encoding antibiotic resistance, and the transport and bacterial mobilization protein, were identified in the sequenced isolates. Ten plasmid replicons were identified, with IncFIB prevalent in 53% of isolates. Combined Illumina and Oxford nanopore sequencing revealed blaNDM-5 on an IncFIA/IncFIC plasmid and is identical to those reported in the USA, Myanmar, and Tanzania. Conclusions: These findings highlight the environmental prevalence of high-risk and WHO-priority pathogens with clinically important ARGs, underscoring the need for a One Health approach to mitigate ARB isolates.
Keywords: Pakistan; antibiotic resistance; carbapenem; plasmid; wastewater; whole-genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- WHO . List of Drug-Resistant Bacteria Most Threatening to Human Health Available. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2024.
-
- Mohsin M., Azam M., ur Rahman S., Esposito F., Sellera F.P., Monte D.F., Cerdeira L., Lincopan N. Genomic background of a colistin-resistant and highly virulent MCR-1-positive Escherichia coli ST6395 from a broiler chicken in Pakistan. Pathog. Dis. 2019;77:ftz064. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftz064. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

