High-Sensitivity Troponin: Finding a Meaningful Delta
- PMID: 39452288
- PMCID: PMC11508916
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd11100318
High-Sensitivity Troponin: Finding a Meaningful Delta
Abstract
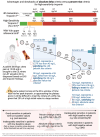
High-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) assays have significantly refined the resolution of biomarker-level detection and have emerged as the gold standard cardiac biomarker in evaluating myocardial injury. Since its introduction, hs-cTn has been integrated into the Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction and various European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) guidelines for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain syndromes. However, despite its integral role in caring for patients with chest pain, there are still substantive gaps in our knowledge of the clinical interpretation of dynamic changes in hs-cTn values. Whether a relative or absolute hs-cTn delta should be used to detect acute myocardial injury remains debatable. There are also emerging considerations of possible sex and racial/ethnic differences in clinically significant troponin deltas. In the emergency department, there is debate about the optimal time frame to recheck hs-cTn after symptom onset for myocardial infarction rule-out and whether hs-cTn deltas should be integrated into clinical risk scores. In this review, we will provide an overview of the history of clinical utilization of cardiac biomarkers, the development of hs-cTn assays, and the ongoing search for a meaningful delta that can be clinically applicable.
Keywords: cardiac biomarkers; high-sensitivity cardiac troponin; troponin delta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Thygesen K., Alpert J.S., Jaffe A.S., Chaitman B.R., Bax J.J., Morrow D.A., White H.D. The Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/World Heart Federation (WHF) Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (2018) Circulation. 2018;138:e618–e651. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000617. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gulati M., Levy P.D., Mukherjee D., Amsterdam E., Bhatt D.L., Birtcher K.K., Blankstein R., Boyd J., Bullock-Palmer P., Conejo T., et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the Evaluation and Diagnosis of Chest Pain. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021;78:e187–e285. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.07.053. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

