An Evaluation of the Accuracy of Digital Models-An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 39452441
- PMCID: PMC11506541
- DOI: 10.3390/dj12100313
An Evaluation of the Accuracy of Digital Models-An In Vitro Study
Abstract
Background: Intraoral scanning technology has opened new perspectives in dental practice, and combined with CAD/CAM technology, contributes significantly to fabricating high-quality prosthetic restorations. Our in vitro study aims to assess the accuracy of digital models obtained from one laboratory and two less commonly used intraoral scanners by conducting 3D measurements on the digital models obtained.
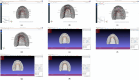
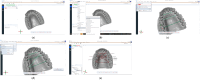
Methods: An articulated simulator cast was used. Forty-eight scans were performed before and after tooth preparation with each scanner. The Zeiss Inspect software (Version: 2023.3.0.969) was used for measurements in sagittal and transversal planes. The obtained values were compared to reference values resulting from manual measurements.
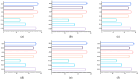
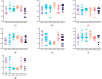
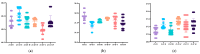
Results: Digital impressions provided discrepancies compared to the reference model. The lowest differences at the A2-L2 (the diagonal dimension of the models from the distal fossa of the second right maxillary molar and the maximum oral convexity of the artificial gingiva at the first left premolar) and the A1-B1 (transversal dimension of the model in the posterior area, from the right second molar's occlusal central fossa to the left second molar central fossa) distances were obtained for the upper models, and at the a1-b1 distance for all the lower models, except the non-prepared models scanned with the intraoral scanners (the discrepancies were not statistically significant). The discrepancies increased with the distance from the starting point of the scan.
Conclusion: The number and position of prepared teeth can influence the accuracy of the scans. Distortions can appear in the case of multiple preparations. The scanning protocol and calibration must be optimized for the highest accuracy. Furthermore, in vivo studies are necessary to evaluate the clinical applicability of these findings.
Keywords: accuracy; digital dentistry; digital impression; intraoral scanner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Mhatre S., Gholap P., Kakade P., Srichand R., Joshi M. Evolution of intraoral scanners in dentistry: An overview. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2023;12:4267–4276.
-
- Ben-Izhack G., Rosner O., Zenziper E., Nissan J., Hosary R., Lugassy D., Shely A. Comparison between Conventional and Digital Impres-sions for Determining Axes and Distances of Three Implants in Straight and Curved Lines: An In Vitro Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024;13:2352. doi: 10.3390/jcm13082352. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

