The Impact of Vitamin D on Androgens and Anabolic Steroids among Adult Males: A Meta-Analytic Review
- PMID: 39452471
- PMCID: PMC11506788
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases12100228
The Impact of Vitamin D on Androgens and Anabolic Steroids among Adult Males: A Meta-Analytic Review
Abstract
Background: Recent studies indicate that vitamin D impacts male reproductive function, with deficiency linked to infertility. This review evaluates the effect of vitamin D supplementation on male fertility, focusing on total testosterone, free testosterone, the free androgen index (FAI), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), sex-hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), and estradiol.
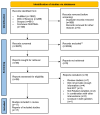
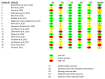
Methods: We systematically searched Medline, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Scopus from their inception until July 2024 for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving adult males. The primary focus of these studies was on reproductive hormone parameters, analyzed using a random-effects meta-analysis and weighted mean difference (WMD). Evidence quality was assessed using ROB2 and GRADE. Meta-regression and dose-response analyses were performed.
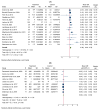
Results: Seventeen studies met the criteria for quantitative analysis. Vitamin D supplementation significantly increased total testosterone levels (WMD 0.38, 95% CI 0.06-0.70, n = 15, I2 = 67.03). However, it had no significant effect on other hormone parameters: free testosterone (WMD 0.00, 95% CI -0.02-0.03, n = 9, I2 = 48.12), FSH (WMD -0.02, 95% CI -0.57-0.53, n = 7, I2 = 48.72), LH (WMD -0.09, 95% CI -0.30-0.12, n = 8, I2 = 0.00), SHBG (WMD 0.73, 95% CI -1.14-2.61, n = 10, I2 = 69.05), FAI (WMD -0.92, 95% CI -2.12-0.27, n = 6, I2 = 0.00), and estradiol (WMD -0.02, 95% CI -2.95-2.92, n = 5, I2 = 20.63).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis shows that vitamin D supplementation may increase total testosterone levels in men. However, further well-designed RCTs are needed to determine vitamin D's effects on other reproductive hormone parameters.
Keywords: estradiol; free androgen index; reproductive hormones; testosterone; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ghasemifard N., Hassanzadeh-Rostami Z., Abbasi A., Naghavi A.M., Faghih S. Effects of vitamin D-fortified oil intake versus vitamin D supplementation on vitamin D status and bone turnover factors: A double blind randomized clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN. 2022;47:28–35. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.12.025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Morvaridzadeh M., Agah S., Alibakhshi P., Heydari H., Hoseini A.S., Palmowski A., Toupchian O., Abdollahi S., Rezamand G., Heshmati J. Effects of calcium and vitamin D co-supplementation on the lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Ther. 2021;43:274–296. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.07.018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

