Apixaban-Induced Esophagitis Dissecans Superficialis-Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 39452506
- PMCID: PMC11506947
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases12100263
Apixaban-Induced Esophagitis Dissecans Superficialis-Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
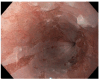
Novel direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are prescribed worldwide in the treatment of non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Adverse reactions have been reported following the use of DOACs. One notable trend in the literature is the growing number of reported cases of esophagitis dissecans superficialis (EDS) generated by DOAC use. We hereby report the case of a 73-year-old woman who presented to the hospital with asthenia, dysphagia, and melena two days prior to admission. The patient had taken apixaban due to non-valvular paroxysmal atrial fibrillation for a few weeks. The biological panel showed moderate anemia with a hemoglobin level of 7.7 g/dL Apixaban-induced EDS was diagnosed by the characteristic endoscopic findings. The patient received treatment with a proton pump inhibitor (pantoprazole) in a double dose. Also, an iron treatment was recommended for a period of six months. The follow-up endoscopy at one month confirmed the healing of the esophageal lesions. The case was discussed with the cardiologist. The first anticoagulant treatment proposed after discharge was a vitamin K antagonist (acenocumarol) but the patient refused this medication and thus it was decided to initiate rivaroxaban. Although DOACs have demonstrated their efficacy in the prevention and treatment of stroke and thromboembolism among the aging demographic, cases of DOAC-induced EDS will continue to pose numerous challenges for physicians worldwide.
Keywords: apixaban; esophagitis dissecans superficialis; upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Rutherford O.W., Jonasson C., Ghanima W., Soderdahl F., Halvorsen S. Comparison of dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban for effectiveness and safety in atrial fibrillation: A nationwide cohort study. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2020;2:75–85. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvz086. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khouja C., Brunton G., Richardson M., Stokes G., Blanchard L., Burchett H., Khatwa M., Walker R., Wright K., Sowden A., et al. Oral anticoagulants: A systematic overview of reviews on efficacy and safety, genotyping, self-monitoring, and stakeholder experiences. Syst. Rev. 2022;1:232. doi: 10.1186/s13643-022-02098-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

