Efficacy and Cognitive Outcomes of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery in Glioblastoma Management for Elderly Patients
- PMID: 39452556
- PMCID: PMC11508357
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm14101049
Efficacy and Cognitive Outcomes of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery in Glioblastoma Management for Elderly Patients
Abstract
Background: Gamma Knife Radiosurgery (GKRS), a specific type of Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS), has developed as a significant modality in the treatment of glioblastoma, particularly in conjunction with standard chemotherapy. The goal of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of combining GKRS with surgical resection and chemotherapy in enhancing therapeutic effects for glioblastoma patients aged 55 years and older.
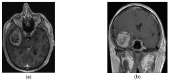
Methods: This prospective clinical study, conducted in accordance with the STROBE guidelines, involved 49 glioblastoma patients aged 55 years and older, treated between January 2013 and January 2023. Data were collected prospectively, and strict adherence to the STUPP protocol was maintained. Only patients who conformed to the STUPP protocol were included in the analysis. Due to concerns regarding the cognitive impairment associated with conventional radiotherapy, and at the patients' request, a radiosurgery plan was offered. Radiosurgery was administered for 4-8 weeks following surgical resection. Any patients who had not received previous radiotherapy received open surgical tumor removal, followed by GKRS along with adjuvant chemotherapy.
Results: In this prospective clinical study of 49 glioblastoma patients aged 55 years and older, the average lifespan post-histopathological diagnosis was established at 22.3 months (95% CI: 12.0-28.0 months). The median time before disease progression was 14.3 months (95% CI: 13.0-29.7 months). The median duration until the first recurrence after treatment was 15.2 months, with documented cases varying between 4 and 33 months. The Gamma Knife Radiosurgery (GKRS) treatment involved a median marginal recommended dose of 12.5 Gy, targeting an average volume of 5.7 cm3 (range: 1.6-39 cm3). Local recurrence occurred in 21 patients, while distant recurrence was identified in 8 patients. Within the cohort, 34 patients were subjected to further therapeutic approaches, including reoperation, a second GKRS session, the administration of bevacizumab and irinotecan, and PCV chemotherapy. A cognitive function assessment revealed that the patients treated with GKRS experienced significantly less cognitive decline compared to the historical controls, who were treated with conventional radiotherapy. The median MMSE scores declined by 1.9 points over 12 months, and the median MoCA scores declined by 2.9 points.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that Gamma Knife Radiosurgery (GKRS), when integrated with surgical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy, offers a substantial benefit for glioblastoma patients aged 55 years and older. The data reveal that GKRS not only prolongs overall survival and progression-free survival but also significantly reduces cognitive decline compared to conventional radiotherapy. These findings underscore the efficacy and safety of GKRS, advocating for its incorporation into standard treatment protocols for older glioblastoma patients. The potential of GKRS to improve patient outcomes while preserving cognitive function is compelling and warrants further research to optimize and confirm its role in glioblastoma management.
Keywords: Gamma Knife Radiosurgery (GKRS); STUPP protocol; cognitive function; elderly patients; glioblastoma; neurocognitive assessment; neurosurgery; oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Nabors L.B., Portnow J., Ahluwalia M., Baehring J., Brem H., Brem S., Butowski N., Campian J.L., Clark S.W., Fabiano A.J., et al. Central Nervous System Cancers, Version 3.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020;18:1537–1570. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2020.0052. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

