Targeting Sodium in Heart Failure
- PMID: 39452570
- PMCID: PMC11508519
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm14101064
Targeting Sodium in Heart Failure
Abstract
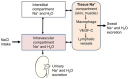
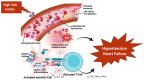
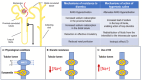
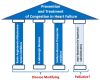
A dominant event determining the course of heart failure (HF) includes the disruption of the delicate sodium (Na+) and water balance leading to (Na+) and water retention and edema formation. Although incomplete decongestion adversely affects outcomes, it is unknown whether interventions directly targeting (Na+), such as strict dietary (Na+) restriction, intravenous hypertonic saline, and diuretics, reverse this effect. As a result, it is imperative to implement (Na+)-targeting interventions in selected HF patients with established congestion on top of quadruple therapy with angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor, β-adrenergic receptor blocker, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, and sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, which dramatically improves outcomes. The limited effectiveness of (Na+)-targeting treatments may be partly due to the fact that the current metrics of HF severity have a limited capacity of foreseeing and averting episodes of congestion and guiding (Na+)-targeting treatments, which often leads to dysnatremias, adversely affecting outcomes. Recent evidence suggests that spot urinary sodium measurements may be used as a guide to monitor (Na+)-targeting interventions both in chronic and acute HF. Further, the classical (2)-compartment model of (Na+) storage has been displaced by the (3)-compartment model emphasizing the non-osmotic accumulation of (Na+), chiefly in the skin. 23(Na+) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) enables the accurate and reliable quantification of tissue (Na+). Another promising approach enabling tissue (Na+) monitoring is based on wearable devices employing ion-selective electrodes for electrolyte detection, including (Na+) and (Cl-). Undoubtably, further studies using 23(Na+)-MRI technology and wearable sensors are required to learn more about the clinical significance of tissue (Na+) storage and (Na+)-related mechanisms of morbidity and mortality in HF.
Keywords: congestion; hypertonic saline; sensors; sodium; urinary spot.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Greene S.J., Bauersachs J., Brugts J.J., Ezekowitz J.A., Lam C.S.P., Lund L.H., Ponikowski P., Voors A.A., Zannad F., Zieroth S., et al. Worsening Heart Failure: Nomenclature, Epidemiology, and Future Directions: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023;81:413–424. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2022.11.023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boorsma E.M., Ter Maaten J.M., Damman K., Dinh W., Gustafsson F., Goldsmith S., Burkhoff D., Zannad F., Udelson J.E., Voors A.A. Congestion in heart failure: A contemporary look at physiology, diagnosis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020;17:641–655. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-0379-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

