In Silico Identification of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (Mpro)
- PMID: 39452758
- PMCID: PMC11510711
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens13100887
In Silico Identification of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (Mpro)
Abstract
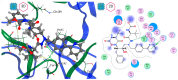
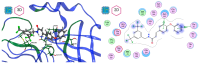
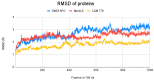
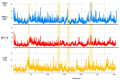
The ongoing Coronavirus Disease 19 (COVID-19) pandemic has had a profound impact on the global healthcare system. As the SARS-CoV-2 virus, responsible for this pandemic, continues to spread and develop mutations in its genetic material, new variants of interest (VOIs) and variants of concern (VOCs) are emerging. These outbreaks lead to a decrease in the efficacy of existing treatments such as vaccines or drugs, highlighting the urgency of new therapies for COVID-19. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to identify potential SARS-CoV-2 antivirals using a virtual screening protocol and molecular dynamics simulations. These techniques allowed us to predict the binding affinity of a database of compounds with the virus Mpro protein. This in silico approach enabled us to identify twenty-two chemical structures from a public database (QSAR Toolbox Ver 4.5 ) and ten promising molecules from our in-house database. The latter molecules possess advantageous qualities, such as two-step synthesis, cost-effectiveness, and long-lasting physical and chemical stability. Consequently, these molecules can be considered as promising alternatives to combat emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Keywords: 3CLpro; Mpro; Nsp5; SARS-CoV-2; antivirals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Repurposing FDA-approved drugs for COVID-19: targeting the main protease through multi-phase in silico approach.Antivir Ther. 2024 Dec;29(6):13596535241305536. doi: 10.1177/13596535241305536. Antivir Ther. 2024. PMID: 39639531
-
In silico identification of D449-0032 compound as a putative SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Aug;42(12):6440-6447. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2234045. Epub 2023 Jul 9. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37424215
-
Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: A Computational Drug Repurposing Study.Arch Med Res. 2021 Jan;52(1):38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.09.013. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Arch Med Res. 2021. PMID: 32962867 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (Mpro) as Anti-Coronavirus Agents.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 4;14(7):797. doi: 10.3390/biom14070797. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Mpro: A Potential Target for Peptidomimetics and Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 19;11(4):607. doi: 10.3390/biom11040607. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33921886 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- W.H.O Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19. 15 July 2024. [(accessed on 17 July 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-epidemiological-update-....
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

